Neuroendocrine cancer, though rare, is a complex and often misunderstood disease. It arises from neuroendocrine cells, which are found throughout the body and have traits of both nerve cells and hormone-producing cells. Because these cells are widespread, neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) can develop in various organs, including the lungs, pancreas, intestines, and more. Recognizing neuroendocrine cancer symptoms early can be challenging, as they often mimic other common conditions. However, understanding these symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the signs and symptoms of neuroendocrine cancer, explore how they vary depending on the tumor’s location, and provide actionable insights to help you or your loved ones stay informed. Whether you’re seeking answers for yourself or someone else, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to take the next steps confidently. Let’s get started.
What Are Neuroendocrine Tumors (NETs)?
Before we delve into the symptoms, it’s essential to understand what neuroendocrine tumors are. These tumors originate from neuroendocrine cells, which play a role in producing hormones and regulating bodily functions. NETs can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and their behavior can range from slow-growing to aggressive.
One of the unique aspects of NETs is their ability to produce hormones. This characteristic often leads to a variety of symptoms, some of which can be subtle and easily overlooked. The location of the tumor significantly influences the type of symptoms a person may experience. For instance, a pancreatic NET may cause different symptoms than a lung NET.
Common Neuroendocrine Cancer Symptoms
The symptoms of neuroendocrine cancer can be broadly categorized into two types: functional and non-functional. Functional tumors produce hormones that cause specific symptoms, while non-functional tumors do not produce hormones and may only cause symptoms as they grow and press on surrounding tissues.
Here’s a breakdown of the most common symptoms associated with neuroendocrine cancer:
1. Hormone-Related Symptoms (Functional Tumors)
Functional tumors can cause a range of symptoms depending on the type of hormone they produce. Some of the most common hormone-related symptoms include:
- Flushing: Sudden redness and warmth in the face and neck.
- Diarrhea: Frequent, watery stools that may be difficult to control.
- Wheezing or Shortness of Breath: Often mistaken for asthma or other respiratory conditions.
- Rapid Heartbeat: Unexplained palpitations or a racing heart.
- Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia): Symptoms like dizziness, sweating, and confusion.
- Weight Loss: Unintentional and unexplained weight loss.
2. Tumor-Related Symptoms (Non-Functional Tumors)
Non-functional tumors may not cause noticeable symptoms until they grow large enough to affect nearby organs or tissues. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal Pain: Persistent pain or discomfort in the abdomen.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, often due to a tumor blocking the bile duct.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Often caused by pressure on the digestive system.
- Fatigue: A general feeling of tiredness or weakness.
- Lumps or Masses: A noticeable lump in the affected area.
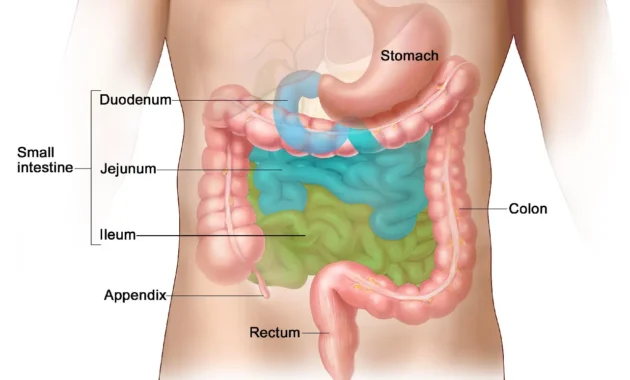
Symptoms Based on Tumor Location
The location of the neuroendocrine tumor plays a significant role in determining the symptoms. Below is a table summarizing the symptoms based on common tumor locations:
| Tumor Location | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Pancreas | Weight loss, abdominal pain, jaundice, low blood sugar, diarrhea |
| Lungs | Wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, chest pain, flushing |
| Stomach/Intestines | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, weight loss |
| Appendix | Appendicitis-like symptoms, abdominal pain, bloating |
| Rectum | Rectal bleeding, pain during bowel movements, changes in stool habits |
Why Are Neuroendocrine Cancer Symptoms Often Overlooked?
Neuroendocrine cancer symptoms are frequently mistaken for other, more common conditions. For example, flushing and diarrhea might be attributed to menopause or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Similarly, wheezing and shortness of breath could be misdiagnosed as asthma. This overlap in symptoms often leads to delays in diagnosis, which can impact treatment outcomes.
If you or someone you know is experiencing persistent or unexplained symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. Early detection can make a significant difference in managing neuroendocrine cancer effectively.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many of the symptoms listed above can be caused by less serious conditions, certain signs should prompt immediate medical attention. These include:
- Persistent abdominal pain or discomfort.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Frequent diarrhea or flushing.
- Jaundice or changes in stool color.
- A noticeable lump or mass in the body.
If you notice any of these symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. It’s always better to be proactive when it comes to your health.
Diagnosing Neuroendocrine Cancer
Diagnosing neuroendocrine cancer typically involves a combination of imaging tests, blood tests, and biopsies. Some of the most common diagnostic tools include:
- Imaging Tests: CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans can help identify the location and size of the tumor.
- Blood and Urine Tests: These tests can detect elevated levels of hormones or other markers associated with NETs.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample is taken from the tumor and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Neuroendocrine Cancer
The treatment for neuroendocrine cancer depends on several factors, including the tumor’s location, size, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery: Removing the tumor is often the first line of treatment, especially if the cancer is localized.
- Medication: Hormone therapy or targeted drugs can help manage symptoms and slow tumor growth.
- Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: In some cases, chemotherapy may be used to treat aggressive or advanced NETs.
Living with Neuroendocrine Cancer
A diagnosis of neuroendocrine cancer can be overwhelming, but many people continue to lead fulfilling lives with proper treatment and support. Here are a few tips for managing life with NETs:
- Stay Informed: Educate yourself about your condition and treatment options.
- Build a Support Network: Connect with others who are going through similar experiences.
- Follow Your Treatment Plan: Adhere to your healthcare provider’s recommendations and attend regular check-ups.
- Prioritize Self-Care: Take care of your physical and emotional well-being through a balanced diet, exercise, and stress management.
Conclusion
Neuroendocrine cancer is a complex disease with symptoms that can vary widely depending on the tumor’s location and behavior. Recognizing neuroendocrine cancer symptoms early is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment. From hormone-related symptoms like flushing and diarrhea to tumor-related issues such as abdominal pain and weight loss, understanding these signs can empower you to take control of your health.
If you or a loved one is experiencing persistent or unexplained symptoms, don’t wait—seek medical attention. With advancements in diagnostic tools and treatment options, there is hope for managing neuroendocrine cancer and improving quality of life. Stay informed, stay proactive, and remember that you’re not alone in this journey.
Read more:
- Crizotinib Lung Cancer: Advanced Treatment Insights
- Nivolumab for Head and Neck Cancer: A Breakthrough in Immunotherapy
- Treatment for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: New Hope and Innovative Approaches
- Stem Cell Therapy for Lung Cancer: A Revolutionary Approach to Treatment
- Proton Therapy for Lung Cancer: An Advanced Treatment Approach