How Bad is Neuroendocrine Cancer? Understanding the Severity and Outlook
Neuroendocrine cancer is a rare and often misunderstood disease that affects the neuroendocrine system, a network of cells responsible for producing hormones and regulating bodily functions. If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with this condition, you might be wondering, “How bad is neuroendocrine cancer?” The answer isn’t straightforward, as the severity of this cancer can vary widely depending on factors like the tumor’s location, size, and whether it has spread. In this article, we’ll explore the complexities of neuroendocrine cancer, its prognosis, and what you can expect moving forward.
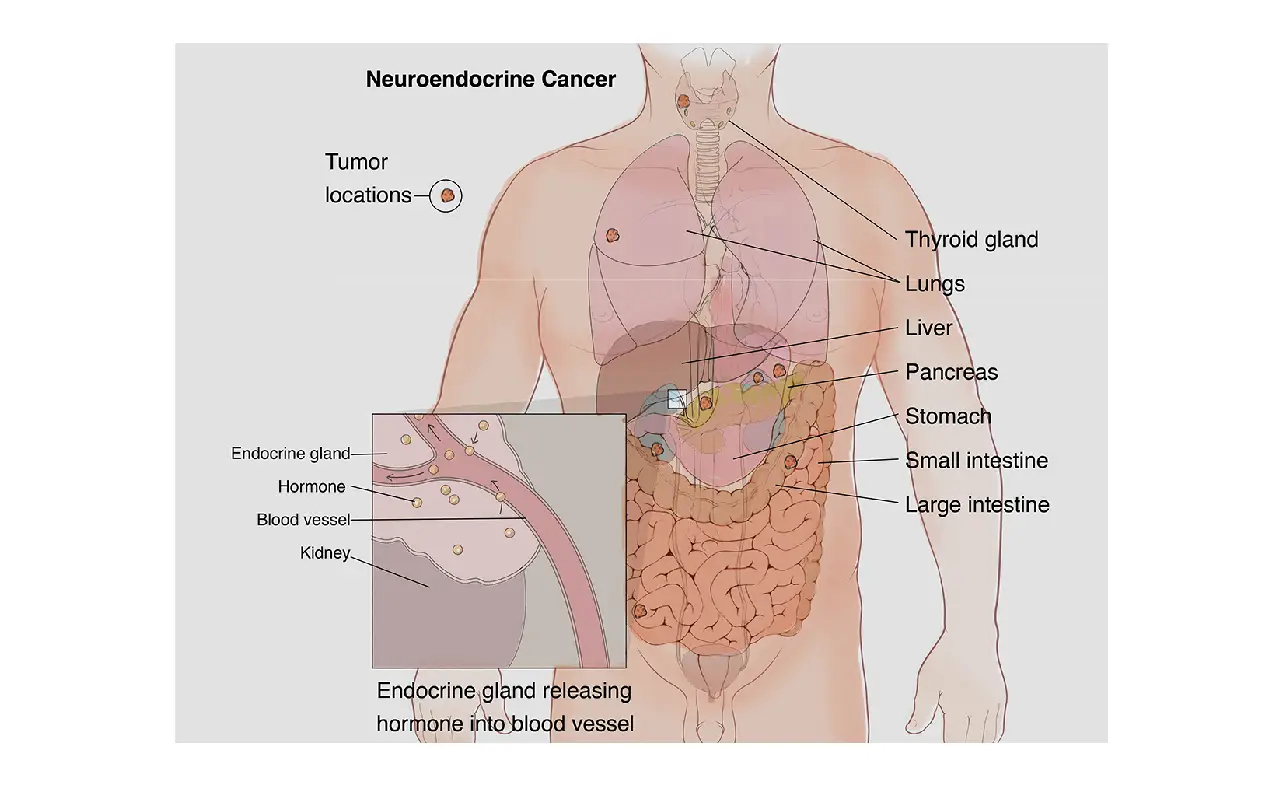
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) can develop in various parts of the body, including the lungs, pancreas, intestines, and other organs. Some tumors grow slowly and may not cause symptoms for years, while others can be aggressive and spread quickly. This variability makes it challenging to generalize the severity of neuroendocrine cancer. However, understanding the disease’s behavior, treatment options, and survival rates can provide clarity and hope for patients and their families.
So, how bad is neuroendocrine cancer? Let’s break it down step by step, from diagnosis to treatment and beyond.
What is Neuroendocrine Cancer?
Neuroendocrine cancer arises from neuroendocrine cells, which are found throughout the body and play a role in hormone production and regulation. These cells act as a bridge between the nervous and endocrine systems, helping to control processes like digestion, metabolism, and stress response. When these cells become cancerous, they can form tumors that may or may not produce excess hormones.
The severity of neuroendocrine cancer depends on several factors, including:
- Tumor Grade: How abnormal the cancer cells look under a microscope (low-grade, intermediate-grade, or high-grade).
- Tumor Stage: Whether the cancer is localized, regional, or metastatic (spread to other parts of the body).
- Tumor Location: Where the tumor is located, such as the pancreas, lungs, or gastrointestinal tract.
Understanding these factors is key to determining how aggressive the cancer is and what treatment options are available.
How Bad is Neuroendocrine Cancer? A Look at Prognosis
The prognosis for neuroendocrine cancer varies widely depending on the tumor’s characteristics. Here’s a breakdown of what you need to know:
1. Low-Grade Tumors
Low-grade neuroendocrine tumors are typically slow-growing and less aggressive. Patients with these tumors often have a better prognosis, especially if the cancer is detected early and treated effectively. In some cases, low-grade tumors may not cause symptoms for years, allowing patients to live relatively normal lives.
2. Intermediate-Grade Tumors
Intermediate-grade tumors fall somewhere between low-grade and high-grade in terms of aggressiveness. These tumors may grow faster than low-grade tumors but are still treatable with surgery, medication, or other therapies.
3. High-Grade Tumors
High-grade neuroendocrine tumors are the most aggressive and can spread quickly to other parts of the body. These tumors are often more challenging to treat and may require a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Survival Rates for Neuroendocrine Cancer
Survival rates provide a general idea of how long patients with neuroendocrine cancer may live after diagnosis. However, it’s important to remember that these rates are based on averages and don’t predict individual outcomes. Here’s a table summarizing the 5-year survival rates for neuroendocrine cancer based on the tumor’s stage:
| Stage | 5-Year Survival Rate | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Localized | 95% | Cancer is confined to the primary site and has not spread. |
| Regional | 75% | Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or tissues. |
| Metastatic | 25% | Cancer has spread to distant organs, such as the liver or lungs. |
These statistics highlight the importance of early detection and treatment. The earlier neuroendocrine cancer is diagnosed, the better the chances of successful treatment and long-term survival.
Symptoms and Diagnosis: What to Watch For
Neuroendocrine cancer is often called a “silent disease” because its symptoms can be vague and easily mistaken for other conditions. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Flushing or redness of the skin
- Diarrhea or abdominal pain
- Wheezing or shortness of breath
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. Diagnostic tests for neuroendocrine cancer may include blood tests, imaging studies (such as CT scans or MRIs), and biopsies.
Treatment Options for Neuroendocrine Cancer
The treatment plan for neuroendocrine cancer depends on the tumor’s grade, stage, and location. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for localized neuroendocrine tumors. Surgery aims to remove the tumor and any affected surrounding tissue.
- Radiation Therapy: Used to target and destroy cancer cells, often in cases where surgery isn’t an option.
- Chemotherapy: Medications that kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that specifically target cancer cells without harming healthy tissue.
- Hormone Therapy: Used to manage symptoms caused by hormone-producing tumors.
Your healthcare team will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan based on your unique diagnosis and needs.
Living with Neuroendocrine Cancer: Tips for Patients and Caregivers
A neuroendocrine cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, but there are steps you can take to manage the disease and maintain your quality of life. Here are some tips:
- Stay Informed: Educate yourself about your diagnosis and treatment options. Knowledge is power!
- Build a Support Network: Lean on family, friends, and support groups for emotional and practical support.
- Follow Your Treatment Plan: Adhere to your healthcare provider’s recommendations and attend all follow-up appointments.
- Prioritize Self-Care: Focus on nutrition, exercise, and mental health to support your overall well-being.
Conclusion
So, how bad is neuroendocrine cancer? The answer depends on various factors, including the tumor’s grade, stage, and location. While some neuroendocrine tumors are slow-growing and highly treatable, others can be aggressive and challenging to manage. Early detection and personalized treatment are key to improving outcomes and quality of life for patients.
- Understanding Neuroendocrine Cancer ICD 10: A Comprehensive Guide
- Stage 4 Neuroendocrine Cancer Spread to Liver Life Expectancy: What You Need to Know
- Stage 4 Neuroendocrine Cancer Life Expectancy: What You Need to Know
- Understanding Neuroendocrine Lung Cancer: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options