Esophageal Cancer Spreads to The Lungs 2026
Stagescancer.net - Esophageal cancer is a malignant disease that affects the esophagus, the tube connecting the throat to the stomach. Unfortunately, in some cases, the cancer can spread or metastasize to other parts of the body, including the lungs. This advanced stage of esophageal cancer, called lung metastasis, presents unique challenges for patients and their healthcare providers.
In this article, we will delve into the implications of esophageal cancer spreading to the lungs. We will explore the common symptoms that may arise, the available treatment options, and the prognosis for patients facing this stage of the disease.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of lung metastasis is crucial for early detection and prompt intervention. We will discuss the specific symptoms that may indicate the spread of esophageal cancer to the lungs and highlight the importance of regular monitoring by healthcare professionals.
When lung metastasis is suspected, various diagnostic tests can help confirm the presence of cancer cells in the lungs. Imaging tests and biopsies are commonly used to identify and assess the extent of metastasis.
Effective treatment strategies for esophageal cancer with lung metastasis are essential in improving patient outcomes. In this article, we will explore the available treatment options, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
Prioritizing the physical and emotional well-being of patients, we will also discuss the role of palliative care and supportive measures in managing esophageal cancer with lung metastasis. Additionally, we will guide lifestyle modifications and support networks that can positively impact patients' overall quality of life.
To provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of the topic, we will highlight ongoing clinical trials and emerging therapies specifically focused on treating lung metastasis in patients with esophageal cancer. We will also address the emotional and psychological impact of the disease, offering coping strategies and resources for patients and their loved ones.
Finally, we will conclude this article by summarizing the key points discussed throughout, emphasizing the importance of early detection, the range of treatment options available, and the need for ongoing support for patients with esophageal cancer that has spread to the lungs.
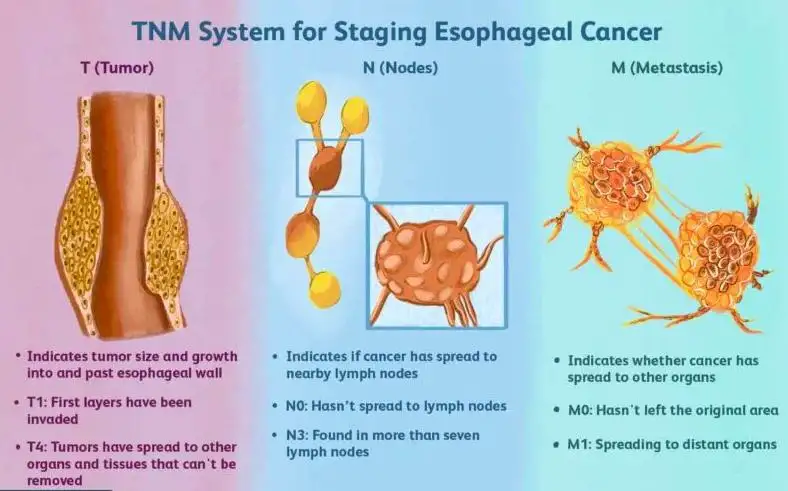
Understanding Esophageal Cancer and Metastasis
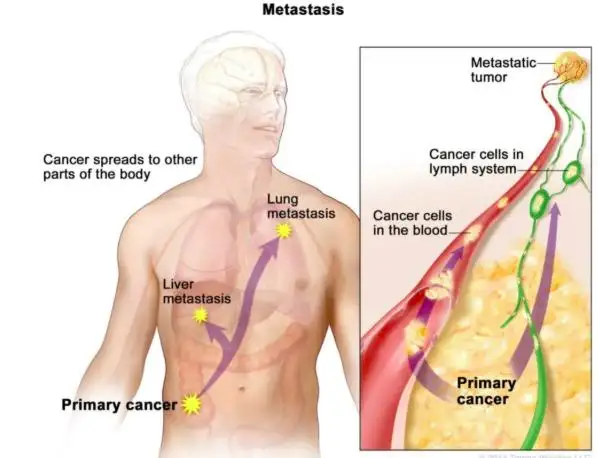
Before exploring the spread of esophageal cancer to the lungs, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the disease itself and the process of metastasis. Esophageal cancer is a malignant tumor that originates in the esophagus, the muscular tube that connects the throat and stomach. It is characterized by abnormal cell growth that can invade nearby tissues and potentially spread to distant organs.
Metastasis refers to the process by which cancer cells break away from the primary tumor, enter the bloodstream or lymphatic system, and establish new tumors in distant parts of the body. The ability of cancer cells to metastasize is a significant factor in determining the stage and prognosis of esophageal cancer.
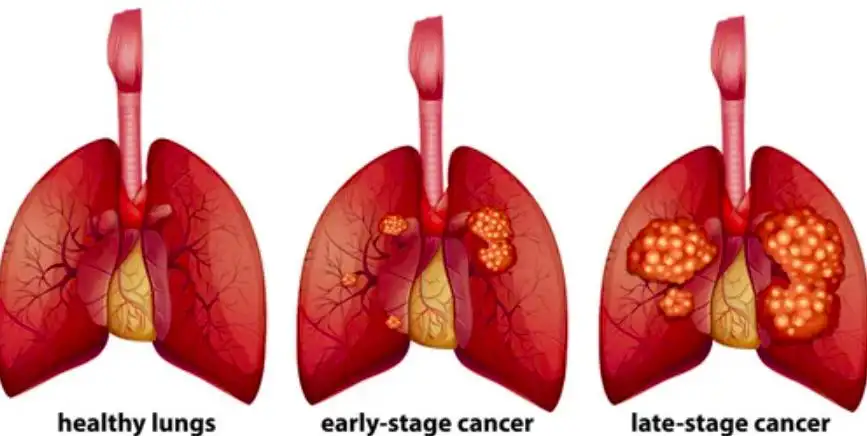
Esophageal cancer most commonly spreads to nearby lymph nodes, the liver, or the lungs. When it spreads to the lungs, it is known as lung metastasis. The lung is one of the most common sites for the spread of esophageal cancer, and this occurrence can significantly impact the course of treatment and overall prognosis.
Understanding the metastasis process is essential in the management and treatment of esophageal cancer patients. By comprehending how cancer cells spread from the primary site to distant organs like the lungs, healthcare professionals can develop targeted treatment strategies to improve patient outcomes.
Factors Affecting Esophageal Cancer Metastasis
| Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Tumor Stage | The extent of cancer growth within the esophagus and nearby tissues affects the likelihood of metastasis. |
| Lymph Node Involvement | Cancer cells that have spread to nearby lymph nodes increase the risk of further metastasis. |
| Tumor Grade | High-grade tumors, which are more aggressive and rapidly growing, have a higher chance of metastasis. |
| Lymphatic and Blood Vessel Invasion | Esophageal tumors that have invaded lymphatic or blood vessels are more likely to metastasize. |
| Presence of Genetic Alterations | Specific genetic mutations and alterations can increase the metastatic potential of esophageal cancer. |
By studying these factors and understanding the metastasis process, researchers and healthcare professionals work towards developing more effective treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes in cases of esophageal cancer with lung metastasis.
Signs and Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer Spread to Lungs
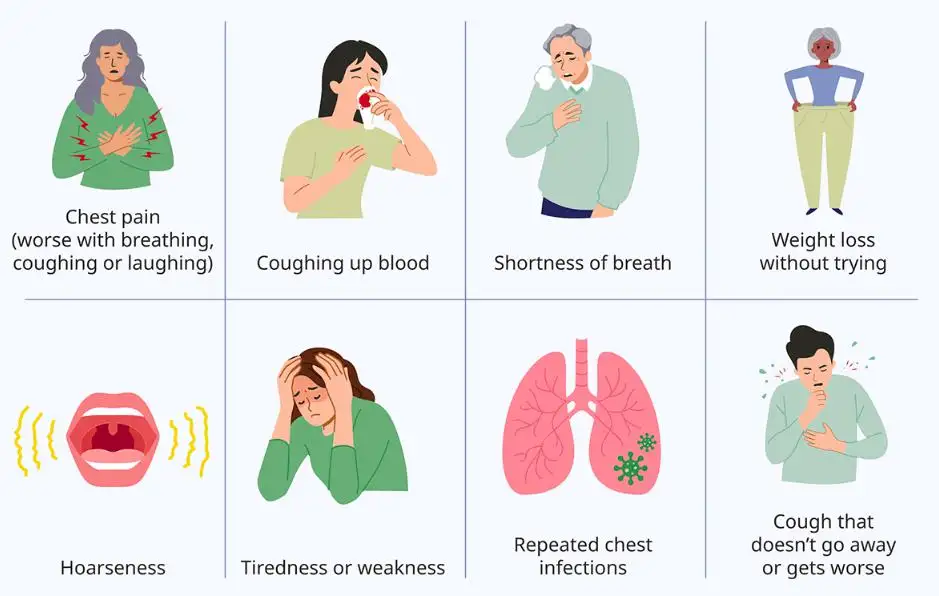
Early detection plays a crucial role in effectively managing esophageal cancer that has spread to the lungs. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of lung metastasis in patients with esophageal cancer is essential for timely intervention and improved outcomes. Here are some common symptoms that may indicate the spread of esophageal cancer to the lungs:
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling short of breath, even during routine activities.
- Chest pain: Persistent or worsening chest pain that may worsen with deep breathing or coughing.
- Coughing: A persistent cough that doesn't go away and may produce blood-tinged sputum.
- Hoarseness: Changes in the voice, such as hoarseness or persistent throat irritation.
- Unintentional weight loss: Significant weight loss without any apparent cause or changes in diet or exercise.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or weak, even with adequate rest and sleep.
- Chest discomfort: Discomfort or pressure in the chest that may radiate to the back or shoulders.
If you experience any of these symptoms or have concerns about your health, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider for further evaluation.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Shortness of breath | Difficulty breathing or feeling short of breath, even during routine activities. |
| Chest pain | Persistent or worsening chest pain that may worsen with deep breathing or coughing. |
| Coughing | A persistent cough that doesn't go away and may produce blood-tinged sputum. |
| Hoarseness | Changes in the voice, such as hoarseness or persistent throat irritation. |
| Unintentional weight loss | Significant weight loss without any apparent cause or changes in diet or exercise. |
| Fatigue | Feeling tired or weak, even with adequate rest and sleep. |
| Chest discomfort | Discomfort or pressure in the chest that may radiate to the back or shoulders. |
It's important to note that these symptoms can also be attributed to other conditions, and the presence of these symptoms does not necessarily mean that the cancer has spread to the lungs. However, if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to discuss them with your healthcare provider for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Diagnostic Tests for Identifying Lung Metastasis from Esophageal Cancer
When lung metastasis is suspected in patients with esophageal cancer, diagnostic tests play a critical role in confirming the spread to the lungs. These tests help healthcare professionals make an accurate diagnosis and formulate an appropriate treatment plan based on the extent of the metastasis. Let's explore some of the commonly used diagnostic tools for identifying lung metastasis from esophageal cancer:
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are typically the first step in evaluating lung metastasis. They allow doctors to visualize the lungs and identify any abnormal growths or masses. Common imaging tests used for this purpose include:
- Chest X-ray: A simple and non-invasive test that produces images of the chest, including the lungs.
- Computed Tomography (CT) scan: Provides detailed cross-sectional images of the lungs, enabling doctors to detect the presence of metastases.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan: Uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the lungs, providing a more comprehensive view than a CT scan in certain cases.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan: Helps identify areas of increased metabolic activity in the lungs, indicating the presence of cancer cells.
Biopsy
A biopsy is a procedure that involves the removal of a sample of lung tissue for examination under a microscope. It is crucial for confirming the presence of cancer cells in the lungs and determining their origin from esophageal cancer. There are different techniques used to perform a lung biopsy, including:
- Needle biopsy: A thin needle is inserted through the chest wall or guided by imaging techniques to obtain a tissue sample from the lung.
- Bronchoscopy: A flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the airways through the mouth or nose to collect tissue samples.
- Thoracoscopy: A small incision is made in the chest wall, and a thin tube with a camera is inserted to visualize and obtain tissue samples from the lung.
These diagnostic tests, in combination with the patient's medical history and physical examination, provide valuable information for healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose lung metastasis in patients with esophageal cancer. Early detection of lung metastasis is crucial for determining appropriate treatment options and improving overall outcomes for patients.
Treatment Options for Esophageal Cancer Spread to Lungs
When esophageal cancer spreads to the lungs, it necessitates a comprehensive treatment approach. Successful management of lung metastasis requires a combination of different treatment modalities, tailored to the individual patient's condition. The available treatment options for esophageal cancer with lung metastasis include:
- Surgery: In select cases, surgical intervention may be considered to remove lung metastases caused by esophageal cancer. This approach aims to eliminate cancerous growths in the lungs and potentially improve the patient's prognosis.
- Chemotherapy: Systemic chemotherapy is frequently utilized to treat esophageal cancer that has spread to the lungs. This treatment involves the administration of anti-cancer drugs to target and kill cancer cells throughout the body, including the lungs.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy utilizes high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells. It can be employed as a primary treatment to alleviate symptoms or as an adjuvant therapy alongside surgery or chemotherapy.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy is a precision medicine approach that targets specific genetic or molecular alterations in cancer cells. It aims to disrupt the growth and spread of cancer cells, with some targeted therapies showing promise in managing esophageal cancer with lung metastasis.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy enhances the body's immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. It has revolutionized cancer treatment and is being investigated as a potential option for patients with advanced esophageal cancer, including lung metastasis.
It is important to note that the choice of treatment options varies depending on several factors, such as the stage of esophageal cancer, the extent of lung metastasis, and the patient's overall health. A multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including oncologists, surgeons, and radiation oncologists, collaborates to develop an individualized treatment plan tailored to each patient's needs.
Surgical Approaches for Lung Metastasis Removal in Esophageal Cancer Patients
For some patients with esophageal cancer that has spread to the lungs, surgical intervention may be recommended to remove the lung metastases. The goal of this surgical approach is to eliminate the cancerous growths in the lungs and potentially improve the patient's prognosis. There are several surgical techniques used in these cases, each with its own benefits and considerations.
1. Wedge Resection:
Wedge resection involves removing the tumor and a small surrounding portion of healthy lung tissue. This procedure is suitable for patients with small metastatic lesions that are confined to a specific area of the lung. It is considered a less invasive option compared to other surgical approaches and may result in faster recovery times.
2. Segmentectomy:
In a segmentectomy procedure, a larger portion of the lung is removed along with the tumor. This technique is typically used when the metastatic lesions are larger or located in multiple segments of the lung. Segmentectomy preserves more lung function compared to a full lobectomy, which can be beneficial for patients with compromised lung function.
3. Lobectomy:
Lobectomy involves the removal of an entire lobe of the lung that contains the metastatic lesions. This procedure is commonly performed when the cancer has spread extensively within a specific lobe or if there are multiple metastatic sites within the same lobe. While lobectomy results in the removal of a larger portion of the lung, it offers the highest chance of complete tumor eradication.
4. Pneumonectomy:
In cases where the metastatic lesions are widespread throughout the lung or involve multiple lobes, a pneumonectomy may be necessary. Pneumonectomy involves the removal of the entire lung affected by the metastasis. This is the most extensive surgical procedure and is typically reserved for patients with advanced disease who can tolerate the removal of an entire lung.
After the surgical removal of lung metastases in esophageal cancer patients, follow-up treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapy may be recommended to target any remaining cancer cells. It is important for patients to discuss with their healthcare team the surgical approach that is most suitable for their specific case and to understand the potential risks and benefits involved.
| Surgical Approach | Patient Suitability | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wedge Resection | Small metastatic lesions confined to a specific area of the lung | Less invasive, faster recovery | May not be suitable for larger or multiple metastatic lesions |
| Segmentectomy | Large or multiple metastatic lesions involving several segments of the lung | Preserves more lung function compared to lobectomy | May still result in reduced lung function |
| Lobectomy | Extensive metastatic spread within a specific lobe or multiple metastatic sites within the same lobe | Highest chance of complete tumor eradication | Removal of a larger portion of the lung |
| Pneumonectomy | Widespread metastatic lesions throughout the lung or involving multiple lobes | Complete removal of affected lung | Loss of an entire lung |
Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy for Esophageal Cancer with Lung Metastasis
When esophageal cancer spreads to the lungs, it presents a significant challenge in terms of treatment and management. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are two essential components of the therapeutic approach for patients with lung metastasis resulting from esophageal cancer. These treatments aim to control the disease, alleviate symptoms, and improve overall outcomes.
Chemotherapy for Lung Metastasis
Chemotherapy involves the administration of powerful drugs that target and destroy cancer cells. In the case of esophageal cancer with lung metastasis, chemotherapy plays a crucial role in reducing tumor size, slowing down cancer progression, and improving quality of life. Different chemotherapy regimens may be used, depending on the specific characteristics of the cancer and the patient's overall health.
Chemotherapy drugs can be administered intravenously or orally, and they circulate throughout the body, targeting cancer cells both in the lungs and elsewhere. This systemic approach is particularly beneficial in cases of metastatic disease. However, chemotherapy does have the potential for side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and a weakened immune system. Close monitoring and supportive care are essential to manage these side effects effectively.
Radiation Therapy for Lung Metastasis
Radiation therapy involves the use of high-energy radiation to target and kill cancer cells. In the context of esophageal cancer with lung metastasis, radiation therapy can be used to shrink tumors in the lungs and alleviate symptoms such as pain and difficulty breathing. It may also be employed as a palliative treatment to improve the patient's quality of life.
External beam radiation therapy is the most common form of radiation treatment for lung metastasis. It delivers precise, targeted doses of radiation to the tumor site, while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. This treatment approach is typically administered over multiple sessions, allowing the body time to recover between treatments.
Similar to chemotherapy, radiation therapy can have side effects, including fatigue, skin irritation, and inflammation of the esophagus or lungs. However, measures can be taken to manage these side effects and ensure patient comfort throughout the treatment course.
In some cases, a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be recommended, aiming to maximize treatment effectiveness and control the cancer's spread. This decision is made based on individualized treatment plans tailored to each patient's specific needs and characteristics of the cancer.
It's important to note that while chemotherapy and radiation therapy can be effective in managing esophageal cancer with lung metastasis, they are not curative treatments. These therapies aim to slow down disease progression, relieve symptoms, and improve the patient's quality of life. The response to treatment and overall prognosis will depend on various factors, including the extent of metastasis, the patient's overall health, and the aggressiveness of the cancer.
Targeted Therapy for Esophageal Cancer with Lung Metastasis
When esophageal cancer spreads to the lungs, targeted therapy offers a personalized approach in managing the disease. Unlike traditional chemotherapy that attacks both healthy and cancerous cells, targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules or proteins that are vital for cancer growth and survival. By targeting these specific molecules, targeted therapy can disrupt the growth and spread of cancer cells, while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
This type of therapy is especially beneficial for patients with esophageal cancer and lung metastasis because it allows for a more precise and effective treatment strategy. Targeted therapy drugs are designed to identify and attack cancer cells based on unique characteristics, such as specific gene mutations or protein markers, that are present in the tumor cells.
One example of targeted therapy used in the treatment of esophageal cancer with lung metastasis is the drug trastuzumab (Herceptin). Trastuzumab targets the HER2 protein, which is overexpressed in certain types of esophageal cancer. By blocking the activity of HER2, trastuzumab can slow down the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Benefits of Targeted Therapy for Lung Metastasis
- Increased treatment effectiveness by directly targeting cancer cells
- Reduced side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy
- Personalized treatment based on specific genetic mutations or protein markers
Current Challenges and Future Outlook
While targeted therapy has shown promise in the treatment of esophageal cancer with lung metastasis, there are still challenges to overcome. Some patients may not have identifiable genetic mutations or protein markers that can be targeted by existing drugs, limiting the effectiveness of targeted therapy in these cases.
However, ongoing research and clinical trials are exploring new drugs and treatment approaches that may be effective for a broader range of patients. By identifying additional genetic mutations and protein markers, researchers hope to develop more targeted therapies that can improve outcomes for patients with esophageal cancer and lung metastasis.
In conclusion, targeted therapy provides a personalized treatment approach for patients with esophageal cancer that has spread to the lungs. By targeting specific molecules or proteins involved in cancer growth and survival, targeted therapy can offer increased treatment effectiveness with reduced side effects. While there are challenges to overcome, ongoing research holds the promise of further advancements in targeted therapy for esophageal cancer with lung metastasis.
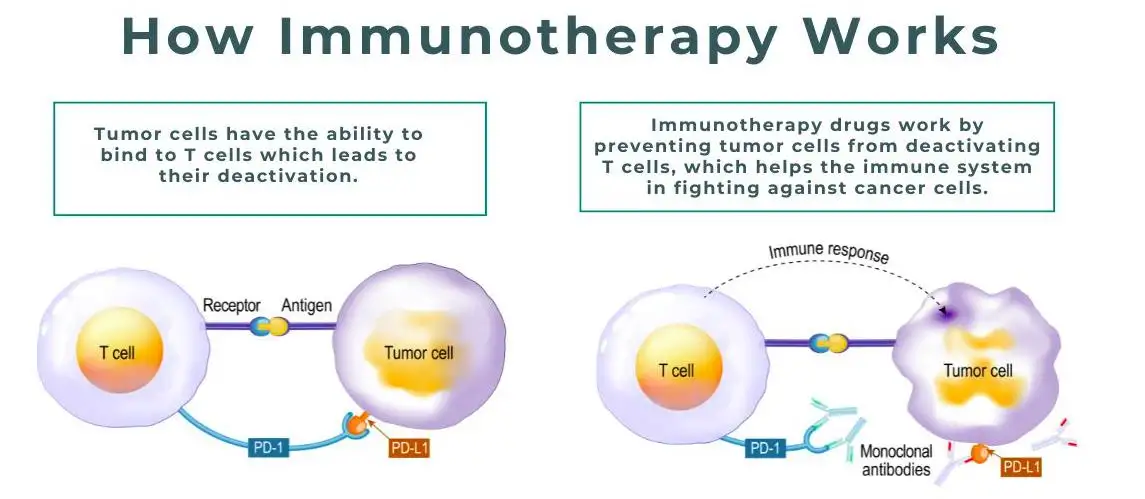
Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Esophageal Cancer Spread to Lungs
In recent years, immunotherapy has emerged as an innovative treatment approach for various types of cancer, including esophageal cancer with lung metastasis. By harnessing the body's immune system to target and destroy cancer cells, immunotherapy offers new hope for patients facing advanced stages of the disease.
Immunotherapy works by boosting the immune system's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells. It does this by either stimulating the immune system directly or by removing the brakes that prevent a robust immune response against cancer. In the context of esophageal cancer spread to the lungs, immunotherapy has shown promising results in improving treatment outcomes and extending survival rates.
There are different types of immunotherapy approaches being used in the treatment of esophageal cancer with lung metastasis, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors and adoptive cell transfer therapies. Immune checkpoint inhibitors block proteins that limit the immune system's ability to attack cancer cells, while adoptive cell transfer therapies involve genetically modifying a patient's own immune cells to enhance their cancer-fighting abilities.
Benefits of Immunotherapy in Esophageal Cancer Treatment
Immunotherapy offers several potential benefits for patients with esophageal cancer that has spread to the lungs. These include:
- Improved response rates: Immunotherapy can enhance the response rates to treatment, increasing the chance of tumor shrinkage and disease control.
- Prolonged survival: Some patients treated with immunotherapy have experienced extended survival times, giving them more quality time with their loved ones.
- Reduced side effects: Compared to traditional treatments like chemotherapy, immunotherapy often has fewer severe side effects, resulting in improved quality of life for patients.
- Potential for long-term remission: In some cases, immunotherapy has led to long-term remission, where cancer remains undetectable even after treatment cessation.
However, it's important to note that not all patients respond the same way to immunotherapy. The effectiveness of this treatment option can vary depending on individual factors, such as the patient's overall health, specific cancer characteristics, and the immune system's response to the treatment.
Comparative Analysis of Immunotherapy Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Mode of Action | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors | Block proteins that inhibit the immune system's response against cancer cells | - Improved response rates - Long-term remission potential |
- Potential side effects - Limited effectiveness in some patients |
| Adoptive Cell Transfer Therapies | Genetically modify and enhance a patient's immune cells for better cancer-fighting abilities | - Potential for prolonged survival - Reduced side effects |
- Complex and expensive procedure - Limited availability |
It's worth mentioning that immunotherapy is an evolving field, with ongoing research and clinical trials exploring new treatment approaches. Collaborating with healthcare professionals and participating in clinical trials can offer patients access to cutting-edge immunotherapy options that may further enhance treatment outcomes.
Overall, immunotherapy holds significant promise in the treatment of esophageal cancer with lung metastasis. While further research is needed to optimize its effectiveness and identify factors that influence treatment response, immunotherapy represents a valuable addition to the arsenal of available treatment options, providing hope and improved prognosis for patients facing advanced stages of the disease.
Prognosis for Esophageal Cancer with Lung Metastasis
Understanding the prognosis for patients with esophageal cancer that has spread to the lungs is crucial for providing realistic expectations. The survival rates, factors influencing prognosis, and potential long-term outcomes will be discussed in this section.
| Prognostic Factors | Survival Rates |
|---|---|
| Stage of esophageal cancer at diagnosis | Varies based on stage (See Table 1) |
| Extent of lung metastasis | Lower survival rates with widespread metastasis |
| Response to treatment | Better response leading to improved prognosis |
| Patient's overall health | Generally, better health yields improved outcomes |
| Stage | 5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|
| Stage I | Approximately 30% |
| Stage II | Approximately 20% |
| Stage III | Approximately 10% |
| Stage IV | Less than 5% |
The prognosis for esophageal cancer with lung metastasis can vary depending on several factors. Early-stage diagnosis and localized lung metastasis generally yield better survival rates. However, advanced stages of the disease and widespread metastasis may result in significantly lower survival rates.
It is important to note that every case is unique, and survival rates are statistical estimates. Factors such as the patient's response to treatment, overall health, and individual circumstances can significantly influence prognosis.
In addition to medical factors, emotional support, and access to palliative care play crucial roles in helping patients manage the challenges associated with esophageal cancer that has spread to the lungs.
Long-Term Outcomes
While the prognosis may seem daunting, advances in medical research and treatment options offer hope for improved long-term outcomes for patients with esophageal cancer and lung metastasis. Ongoing clinical trials and emerging therapies are continuously exploring more effective approaches to managing advanced stages of the disease.
By focusing on early detection, personalized treatment plans, and comprehensive supportive care, healthcare professionals strive to improve survival rates and enhance the quality of life for patients on their journey with esophageal cancer and lung metastasis.
Palliative Care and Supportive Measures for Esophageal Cancer Patients with Lung Metastasis
When esophageal cancer metastasizes to the lungs, the focus of treatment shifts from curative measures to palliative care and supportive strategies. Palliative care aims to improve the quality of life for patients, manage symptoms, and alleviate discomfort caused by the advanced stage of the disease.
Supportive measures play a crucial role in providing comprehensive care for individuals with esophageal cancer and lung metastasis. These measures encompass a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals, including oncologists, palliative care specialists, nurses, social workers, and psychologists. Together, they address the physical, emotional, and psychological needs of patients.
Some of the key components of palliative care and supportive measures include:
- Pain management: Esophageal cancer metastasis to the lungs can cause pain and discomfort. Pain medication, such as opioids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may be prescribed to alleviate pain and improve the patient's overall comfort.
- Symptom control: Lung metastasis can give rise to symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Supportive measures, such as oxygen therapy, respiratory treatments, and pulmonary rehabilitation, can help manage these symptoms and enhance the patient's quality of life.
- Nutritional support: Esophageal cancer can affect the ability to swallow and consume food. Nutritional counseling and intervention by dieticians can optimize the patient's nutritional intake and prevent weight loss, malnutrition, and associated complications.
- Psychological and emotional support: A cancer diagnosis and its progression can take a toll on a patient's mental health. Psychological support, including counseling, support groups, and therapy, can help patients and their families cope with the emotional challenges of living with advanced esophageal cancer.
- Advance care planning: Discussing and documenting preferences for end-of-life care can help patients and their families make important decisions regarding treatment options, resuscitation, and care in the event of clinical deterioration.
Incorporating palliative care and supportive measures into the treatment plan for esophageal cancer patients with lung metastasis is essential to ensure comprehensive, holistic care that addresses all aspects of the patient's well-being.
| Palliative Care and Supportive Measures for Esophageal Cancer Patients with Lung Metastasis | Description |
|---|---|
| Pain management | Prescription of pain medication, such as opioids and NSAIDs, to alleviate pain and improve patient comfort. |
| Symptom control | Implementation of supportive measures like oxygen therapy, respiratory treatments, and pulmonary rehabilitation to manage symptoms like coughing, shortness of breath, and fatigue. |
| Nutritional support | Provision of nutritional counseling and intervention by dieticians to optimize nutritional intake and prevent weight loss, malnutrition, and associated complications. |
| Psychological and emotional support | Offering counseling, support groups, and therapy to help patients and their families cope with the emotional challenges of living with advanced esophageal cancer. |
| Advance care planning | Facilitating discussions and documentation of preferences for end-of-life care, empowering patients to make decisions regarding treatment options and care in the event of clinical deterioration. |
Clinical Trials and Emerging Therapies for Esophageal Cancer with Lung Metastasis
The field of esophageal cancer research is constantly evolving, with ongoing clinical trials and emerging therapies specifically focused on lung metastasis. These advancements hold great promise for improving treatment outcomes and patient survival rates.
Exploring Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new treatment approaches for esophageal cancer with lung metastasis. Through these trials, researchers work to identify innovative therapies that may offer improved outcomes compared to standard treatments.
Patients who participate in clinical trials not only gain access to potentially groundbreaking therapies but also contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge, ultimately benefiting future patients.
Some ongoing clinical trials for esophageal cancer with lung metastasis include:
- A phase III trial comparing the efficacy of a novel targeted therapy with standard chemotherapy in patients with lung metastasis
- A phase II trial assessing the effectiveness of immunotherapy in combination with radiation therapy for reducing lung metastasis in esophageal cancer patients
- A phase I trial evaluating the safety and tolerability of a new experimental drug that targets specific molecular pathways involved in lung metastasis
| Trial Name | Objective | Patient Population | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase III Trial | Comparing targeted therapy and chemotherapy | Patients with esophageal cancer and lung metastasis | Ongoing |
| Phase II Trial | Assessing immunotherapy with radiation therapy | Esophageal cancer patients with lung metastasis | Enrollment underway |
| Phase I Trial | Evaluating safety of experimental drug | Patients with lung metastasis from esophageal cancer | Not yet recruiting |
Emerging Therapies
Besides clinical trials, several emerging therapies show promise for treating esophageal cancer with lung metastasis. These therapies, which are still being researched or undergoing early-stage trials, represent exciting new avenues for targeted treatment.
Emerging therapies for esophageal cancer with lung metastasis include:
- Novel immunotherapies that enhance the body's immune response against cancer cells
- Precision medicine approaches that target specific genetic mutations driving lung metastasis
- Combination therapies that combine multiple treatment modalities for a synergistic effect
While these emerging therapies require further study and validation, they offer hope for improved outcomes and prolonged survival for patients with esophageal cancer and lung metastasis.
Closing Thoughts
Clinical trials and emerging therapies are paving the way for innovative treatment options for esophageal cancer patients with lung metastasis. By participating in clinical trials, patients can access cutting-edge therapies, contribute to medical advancements, and potentially benefit from improved outcomes.
As research continues to progress, it is essential to stay informed about the latest developments in clinical trials and emerging therapies. Consultation with a healthcare provider experienced in treating esophageal cancer with lung metastasis can help patients explore potential participation in clinical trials and access emerging treatment options.
Lifestyle Modifications and Support Networks for Esophageal Cancer Patients
Beyond medical treatments, managing esophageal cancer requires a holistic approach that includes lifestyle modifications and support networks. These additional measures can have a significant impact on the overall well-being of patients, helping them cope with the challenges they face throughout their journey.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting certain lifestyle modifications can help improve the quality of life for esophageal cancer patients. These modifications may include:
- Dietary changes: Working with a registered dietitian to develop a personalized nutrition plan that takes into account the patient's specific needs and challenges, such as difficulty swallowing or maintaining a healthy weight.
- Physical activity: Engaging in regular exercise, as appropriate for the patient's condition, to promote overall strength, cardiovascular health, and mood.
- Stress management: Employing stress reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or other relaxation practices to enhance emotional well-being.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking, if applicable, as smoking can worsen the symptoms and prognosis of esophageal cancer.
Support Networks
Esophageal cancer patients often benefit from the support of various networks, including:
- Family and friends: Establishing a strong support system of loved ones who can provide emotional support, assistance with daily activities, and companionship throughout the treatment process.
- Cancer support groups: Participating in support groups where patients can connect with others facing similar challenges, share experiences, and find a sense of community.
- Online resources: Accessing reputable online platforms that offer information, forums, and resources specifically tailored to esophageal cancer patients.
- Professional counseling: Seeking guidance from trained mental health professionals who specialize in cancer care to address emotional concerns and develop coping strategies.
By integrating lifestyle modifications and leveraging support networks, esophageal cancer patients can enhance their overall well-being and pursue a more active role in their treatment journey.
| Lifestyle Modifications | Support Networks |
|---|---|
| Dietary changes | Family and friends |
| Physical activity | Cancer support groups |
| Stress management | Online resources |
| Smoking cessation | Professional counseling |
Coping with the Emotional and Psychological Impact of Esophageal Cancer Spread to Lungs
Receiving a diagnosis of esophageal cancer with lung metastasis can have a profound emotional impact on patients and their loved ones. Dealing with the physical symptoms and treatment can be overwhelming, and it is essential to address the psychological and emotional challenges that arise. Coping strategies and psychological support play a crucial role in navigating this difficult journey.
1. Seek Professional Counseling
Professional counseling can provide invaluable support and guidance in managing the emotional impact of esophageal cancer with lung metastasis. A qualified therapist or counselor can help patients and their families process their feelings, explore coping mechanisms, and develop healthy strategies for emotional well-being.
2. Join Support Groups
Connecting with others who are going through similar experiences can foster a sense of community and understanding. Joining support groups for patients with esophageal cancer and lung metastasis can provide a safe space to share emotions, gain insights from others, and learn coping strategies from those who have faced similar challenges.
3. Practice Self-Care
Prioritizing self-care is crucial for managing the emotional toll of cancer. Engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation can help reduce stress levels and promote emotional well-being. Whether it's practicing mindfulness, engaging in hobbies, or spending time in nature, taking time for oneself is essential for mental and emotional health.
4. Communicate with Loved Ones
Open and honest communication with loved ones can provide much-needed emotional support. Sharing fears, concerns, and hopes with trusted family members and friends can alleviate feelings of loneliness and foster a sense of connection. Having a support network can make a significant difference in managing the emotional impact of the disease.
5. Educate Yourself
Gaining knowledge and understanding about esophageal cancer and its management can help reduce anxiety and provide a sense of control. Stay informed about the disease, treatment options, and the latest research findings. However, it is important to balance information-seeking with self-care and avoid overwhelming oneself with excessive research.
6. Engage in Relaxation Techniques
Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga, can help reduce stress and promote emotional well-being. These techniques can provide a sense of calm and improve overall mental resilience when facing the challenges of esophageal cancer with lung metastasis.
7. Explore Online Resources
There are numerous online resources available for patients and families affected by esophageal cancer. Websites, forums, and support groups specifically dedicated to esophageal cancer with lung metastasis can offer information, emotional support, and a platform for connecting with others facing similar circumstances.
8. Lean on Healthcare Professionals
Don't hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals for emotional support. Oncologists, nurses, and other members of the healthcare team are experienced in caring for patients with esophageal cancer and can provide guidance, resources, and referrals to appropriate support services.
9. Take Advantage of Palliative Care
Palliative care focuses on improving the quality of life for patients with serious illnesses like esophageal cancer. Palliative care teams can provide specialized support for managing pain, controlling symptoms, and addressing emotional and psychological needs. They work in conjunction with the primary treatment team to enhance overall well-being.
10. Stay Hopeful
While coping with the emotional impact of esophageal cancer with lung metastasis can be challenging, it is important to maintain hope and a positive outlook. Progress in medical research and advancements in treatment options offer hope for improved outcomes and increased survival rates.
| Coping Strategies | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Seeking professional counseling | Guidance and support from a trained therapist or counselor |
| Joining support groups | Connection and understanding from others facing similar circumstances |
| Practicing self-care | Reduced stress levels and enhanced emotional well-being |
| Communicating with loved ones | Emotional support and a sense of connection |
| Educating oneself | Reduced anxiety and increased sense of control |
| Engaging in relaxation techniques | Reduced stress and improved mental resilience |
| Exploring online resources | Access to information, support, and connections with others |
| Leaning on healthcare professionals | Guidance, resources, and support from experienced professionals |
| Utilizing palliative care | Specialized support for pain and symptom management |
| Maintaining hope | Positive outlook and belief in advancements in treatment |
Navigating the Journey: Tips for Patients with Esophageal Cancer Spread to Lungs
When facing the complex journey of esophageal cancer with lung metastasis, patients need practical guidance to navigate the challenges ahead. In this section, we provide valuable tips and advice to help patients effectively manage their condition, prioritize self-care, communicate with healthcare providers, and become advocates for their own well-being. By empowering patients with knowledge and strategies, we strive to improve their overall experience and outcomes.
Self-Care Strategies
- Physical well-being: Engage in regular exercise, eat a balanced diet, and get adequate rest to support your body's strength and resilience. Prioritize activities that bring you joy and help reduce stress.
- Psychological well-being: Seek emotional support from trusted loved ones or join support groups where you can share your experiences. Consider relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga, to promote mental well-being.
- Managing side effects: Stay informed about common side effects of treatment and work closely with your healthcare team to proactively manage them. Follow medication schedules and report any unusual symptoms promptly.
Effective Communication with Healthcare Providers
- Building a trusted relationship: Establish open and honest communication with your healthcare team. Share your concerns, questions, and goals to ensure collaborative decision-making and personalized care.
- Preparing for appointments: Before each medical appointment, write down any questions or symptoms you want to discuss with your healthcare provider. Keep a record of your medications and treatment history for easy reference.
- Seeking clarity: If you don't understand a medical term or need further clarification about your diagnosis or treatment plan, ask your healthcare provider for simple explanations. Request written materials or reliable online resources to supplement your understanding.
Becoming an Advocate
As a patient with esophageal cancer and lung metastasis, you have the right to advocate for your needs and access the best possible care. Consider the following tips to become a proactive advocate for your own well-being:
- Seek second opinions: Don't hesitate to consult with additional specialists to explore different perspectives and treatment options. Second opinions can provide invaluable insights and help you make informed decisions.
- Stay informed about clinical trials: Keep abreast of ongoing clinical trials and emerging therapies that may offer new possibilities for your condition. Discuss potential trial participation with your healthcare provider.
- Connect with support networks: Reach out to patient advocacy organizations and online forums dedicated to esophageal cancer and lung metastasis. Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide emotional support, shared experiences, and valuable resources.
| Support Resources | Contact Information |
|---|---|
| Esophageal Cancer Awareness Association | www.ecaware.org |
| The Esophageal Cancer Education Foundation | www.fightec.org |
| Esophageal Cancer Action Network | www.ecan.org |
By adopting self-care strategies, improving communication with healthcare providers, and becoming an advocate, patients with esophageal cancer spread to the lungs can navigate their journey more confidently. Remember, you are not alone, and there are resources available to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the spread of esophageal cancer to the lungs, known as lung metastasis, poses significant challenges for patients. Early detection is crucial for improving outcomes and providing timely intervention. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of lung metastasis is essential in order to initiate diagnostic tests and confirm the spread of cancer to the lungs.
There are various treatment options available for esophageal cancer patients with lung metastasis. These include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. The choice of treatment depends on individual factors, such as the extent of metastasis and the patient's overall health.
Furthermore, supportive measures, including palliative care and lifestyle modifications, are vital in enhancing the patients' quality of life and managing symptoms. Clinical trials and emerging therapies offer hope for future treatment options, emphasizing the importance of ongoing research in this field. Overall, a multidisciplinary approach involving medical professionals, support networks, and personalized care is crucial to optimize outcomes for patients with esophageal cancer spread to the lungs.
FAQ
What are the symptoms of esophageal cancer spreading to the lungs?
Symptoms of esophageal cancer spreading to the lungs may include coughing up blood, difficulty breathing, chest pain, persistent cough, and fatigue.
How is lung metastasis from esophageal cancer diagnosed?
Diagnostic tests such as imaging tests (CT scan, MRI, PET scan) and biopsies are commonly used to identify lung metastasis from esophageal cancer.
What are the available treatment options for esophageal cancer that has spread to the lungs?
Treatment options for esophageal cancer with lung metastasis may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
Can lung metastasis from esophageal cancer be surgically removed?
In some cases, surgical intervention may be an option to remove lung metastases caused by esophageal cancer. Different surgical approaches and techniques may be employed.
How can chemotherapy and radiation therapy help manage esophageal cancer with lung metastasis?
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can help control the growth of cancer cells in the lungs, alleviate symptoms, and improve overall outcomes for patients with lung metastasis from esophageal cancer.
What is targeted therapy, and how is it used in treating esophageal cancer with lung metastasis?
Targeted therapy is a personalized treatment approach that targets specific genes or proteins involved in cancer cell growth. It can be used to manage lung metastasis in patients with esophageal cancer.
Can immunotherapy be used in the treatment of esophageal cancer spread to the lungs?
Yes, immunotherapy has shown promise as a treatment option for esophageal cancer with lung metastasis. It helps to stimulate the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
What is the prognosis for esophageal cancer patients with lung metastasis?
The prognosis for patients with esophageal cancer that has spread to the lungs can vary depending on various factors. Survival rates and long-term outcomes are influenced by the extent of metastasis and individual patient characteristics.
What is palliative care, and how does it benefit esophageal cancer patients with lung metastasis?
Palliative care focuses on improving the quality of life and providing support for patients with advanced cancer, including those with esophageal cancer and lung metastasis. It helps manage symptoms and provides emotional and practical support.
Are there any clinical trials or emerging therapies specifically for esophageal cancer with lung metastasis?
Yes, ongoing clinical trials and emerging therapies are being investigated for the treatment of lung metastasis in patients with esophageal cancer. These trials explore potential future treatment options.
What lifestyle modifications and support networks can benefit esophageal cancer patients?
Certain lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise, can help support the overall well-being of esophageal cancer patients. Additionally, joining support networks and seeking emotional support can provide valuable resources and guidance.
How can esophageal cancer patients cope with the emotional impact of lung metastasis?
Coping strategies, psychological support, and available resources can help esophageal cancer patients and their loved ones navigate the emotional impact of a lung metastasis diagnosis. Supportive care services and counseling can provide the necessary support.
What tips and advice can help esophageal cancer patients with lung metastasis?
Tips and advice for patients with esophageal cancer and lung metastasis include practicing self-care, maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, and advocating for one's needs. These strategies can help individuals navigate their cancer journey more effectively.