Neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer, though rare, is a complex and often misunderstood form of cancer. It originates in the neuroendocrine cells, which are found throughout the body and play a dual role in both the nervous and endocrine systems. These cells produce hormones that regulate various bodily functions, making this type of cancer particularly challenging to diagnose and treat. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer, providing you with the knowledge to better understand this condition.
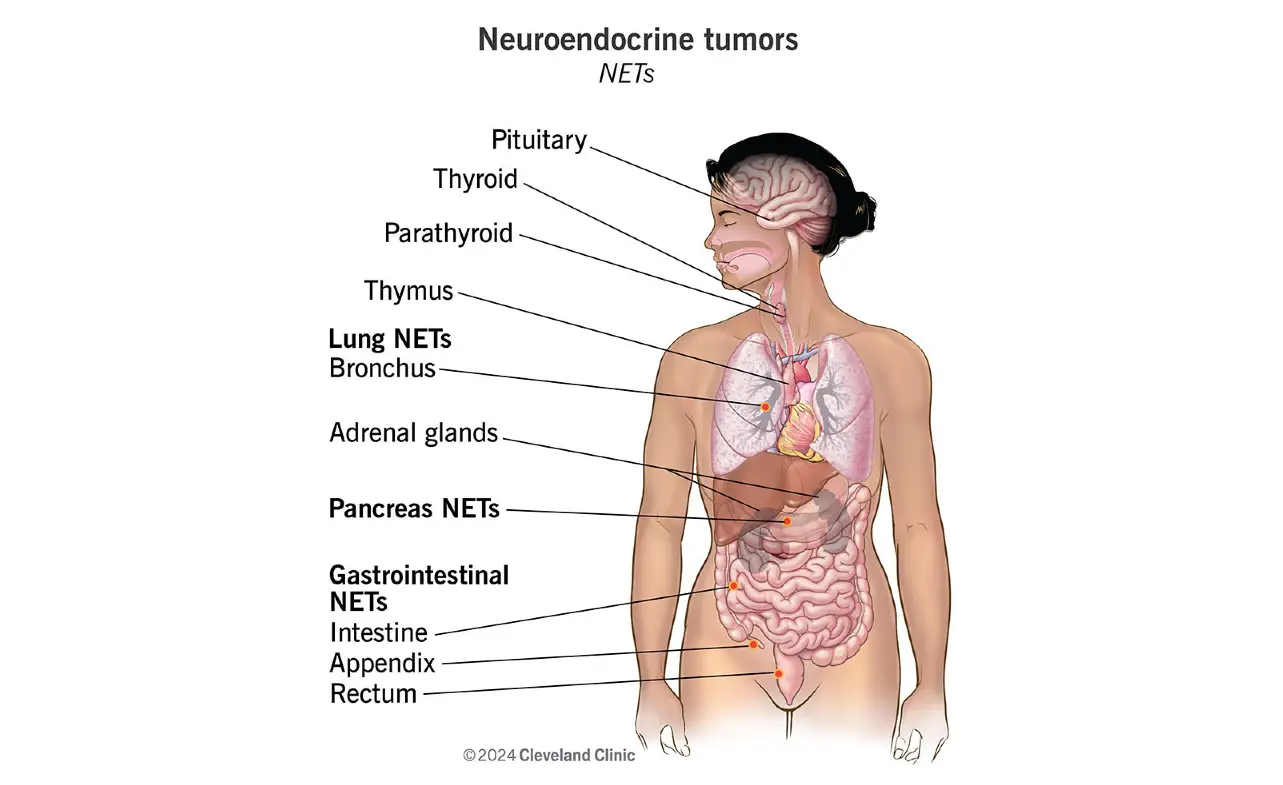
Why is it important to learn about neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer? Because early detection can significantly improve outcomes. Despite accounting for only about 2% of all cancer cases, neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) can affect multiple organs, including the lungs, pancreas, and gastrointestinal tract. Think of your body as a finely tuned machine—when one part malfunctions, the entire system can be thrown off balance. This is precisely what happens with neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer.
What is Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Cancer?
Neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the neuroendocrine cells. These cells are responsible for producing hormones and are found in organs such as the lungs, pancreas, and digestive tract. Neuroendocrine tumors can be benign or malignant, with the latter being more aggressive and potentially life-threatening.
Types of Neuroendocrine Tumors
Neuroendocrine tumors are classified based on their location and behavior. Here’s a quick breakdown:
| Type of Tumor | Common Locations | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Carcinoid Tumors | Lungs, Gastrointestinal Tract | Slow-growing, Less Aggressive |
| Pancreatic NETs | Pancreas | Varies (Can be Aggressive) |
| Small Cell Lung Cancer | Lungs | Highly Aggressive |
| Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma | Lungs, Other Organs | Aggressive |
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer remain unclear, but researchers have identified several risk factors that may increase the likelihood of developing this condition.
Genetic Factors
Certain inherited conditions, such as Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 (MEN1) and Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1), are linked to a higher risk of neuroendocrine tumors. If you have a family history of these conditions, genetic counseling may be beneficial.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain chemicals or toxins, such as asbestos or heavy metals, may increase the risk of developing neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer. Smoking is also a significant risk factor, particularly for small cell lung cancer.
Age and Gender
Neuroendocrine tumors are more commonly diagnosed in individuals aged 50 and older. Additionally, some types of NETs, such as carcinoid tumors, are slightly more prevalent in women.
Symptoms of Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Cancer
The symptoms of neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer can vary widely depending on the tumor’s location and whether it produces excess hormones. This variability often makes diagnosis challenging.
Common Symptoms
- Flushing: Sudden redness and warmth in the face and neck.
- Diarrhea: Persistent diarrhea that doesn’t respond to typical treatments.
- Abdominal Pain: Discomfort or pain in the stomach area.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without changes in diet or exercise.
Hormone-Related Symptoms
- Cushing’s Syndrome: Caused by excess cortisol production, leading to weight gain and high blood pressure.
- Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar levels, resulting in dizziness and fatigue.
- Carcinoid Syndrome: A group of symptoms, including flushing and diarrhea, caused by hormone-secreting tumors.
Diagnosing Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Cancer
Diagnosing neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer requires a combination of imaging tests, biopsies, and laboratory analyses. Due to the nonspecific nature of the symptoms, a thorough diagnostic process is essential.
Imaging Tests
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the tumor and surrounding tissues.
- MRI: Offers high-resolution images, particularly useful for detecting tumors in soft tissues.
- PET Scan: Helps identify metastatic tumors by highlighting areas with high metabolic activity.
Biopsy
A tissue sample is taken from the tumor and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis and determine the tumor’s grade.
Blood and Urine Tests
These tests measure hormone levels and other biomarkers that may indicate the presence of a neuroendocrine tumor.
Treatment Options for Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Cancer
The treatment plan for neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer depends on factors such as the tumor’s location, size, and stage, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Surgery
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for localized tumors. The goal is to remove the tumor entirely, which can be curative in some cases.
Medications
- Somatostatin Analogs: These drugs help control hormone production and alleviate symptoms.
- Targeted Therapy: Medications like everolimus target specific pathways in cancer cells to inhibit their growth.
- Chemotherapy: Used for aggressive or advanced tumors to shrink or slow their progression.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy may be used to target tumors that cannot be surgically removed or to relieve symptoms in advanced cases.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT)
PRRT is a cutting-edge treatment that delivers radiation directly to cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
Living with Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Cancer
A diagnosis of neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer can be overwhelming, but there are ways to manage the condition and maintain a good quality of life.
Lifestyle Changes
- Diet: Eating a balanced diet can help manage symptoms like diarrhea and weight loss.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve energy levels and overall well-being.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation and yoga can help reduce stress and improve mental health.
Support Systems
Joining support groups or connecting with others who have neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Conclusion
Neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer is a rare but complex condition that requires a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, patients and their families can make informed decisions and take proactive steps toward managing the disease. Early detection and personalized treatment plans are key to improving outcomes and quality of life.
If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms that could be related to neuroendocrine carcinoma cancer, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Remember, knowledge is power, and staying informed is the first step toward taking control of your health.
Read more: