Neuroendocrine lung cancer is a rare but complex form of lung cancer that often leaves patients and their families searching for answers. Unlike more common types of lung cancer, neuroendocrine tumors originate from neuroendocrine cells, which are specialized cells that release hormones into the bloodstream. These tumors can be challenging to diagnose and treat, making it crucial to understand their unique characteristics. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what neuroendocrine lung cancer is, its symptoms, how it’s diagnosed, and the latest treatment options available. Whether you’re a patient, caregiver, or simply curious, this guide will provide you with the knowledge you need to navigate this condition.
What Is Neuroendocrine Lung Cancer?
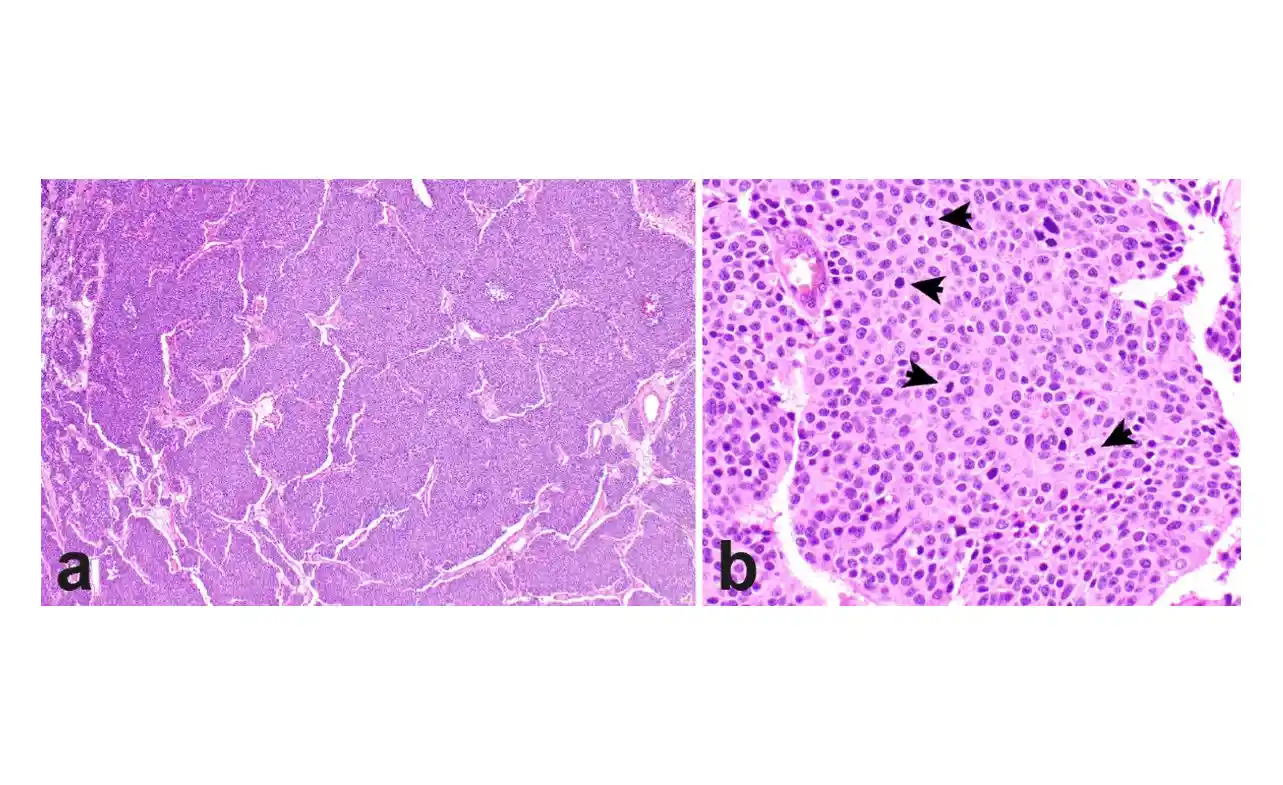
Neuroendocrine lung cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the neuroendocrine cells of the lungs. These cells are part of the neuroendocrine system, which is responsible for producing hormones that regulate various bodily functions. Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) can be classified into different types based on their behavior and growth rate. The most common types include:
- Typical Carcinoid Tumors: These are slow-growing and less aggressive.
- Atypical Carcinoid Tumors: These grow faster and are more likely to spread.
- Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (LCNEC): This is a high-grade, aggressive form of neuroendocrine cancer.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): This is the most aggressive type and is often linked to smoking.
Understanding the type of neuroendocrine lung cancer is critical because it influences the treatment approach and prognosis. But what exactly causes these tumors? Let’s explore.
Causes and Risk Factors of Neuroendocrine Lung Cancer
The exact cause of neuroendocrine lung cancer is still unknown, but several risk factors have been identified. Smoking is the most significant risk factor, particularly for small cell lung cancer. However, non-smokers can also develop neuroendocrine tumors, suggesting that other factors, such as genetics or environmental exposures, may play a role.
Other potential risk factors include:
- Family History: A family history of neuroendocrine tumors may increase your risk.
- Age: Most cases are diagnosed in people over the age of 60.
- Gender: Men are slightly more likely to develop neuroendocrine lung cancer than women.
- Exposure to Carcinogens: Prolonged exposure to asbestos, radon, or other harmful substances may increase the risk.
While these factors can contribute to the development of neuroendocrine lung cancer, it’s important to remember that not everyone with these risk factors will develop the disease. Early detection and awareness are key to improving outcomes.
Symptoms of Neuroendocrine Lung Cancer
Neuroendocrine lung cancer symptoms can vary depending on the type and stage of the tumor. Some patients may experience no symptoms at all, especially in the early stages. However, as the tumor grows or spreads, the following symptoms may occur:
- Persistent Cough: A cough that doesn’t go away or worsens over time.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
- Chest Pain: Pain or discomfort in the chest, often worsened by coughing or deep breathing.
- Wheezing: A whistling sound when breathing, caused by airway obstruction.
- Fatigue: Extreme tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying can be a sign of advanced cancer.
- Hormonal Symptoms: Some neuroendocrine tumors produce hormones, leading to symptoms like flushing, diarrhea, or low blood sugar.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation. Early diagnosis can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Diagnosing Neuroendocrine Lung Cancer
Diagnosing neuroendocrine lung cancer involves a combination of imaging tests, biopsies, and laboratory analyses. Here’s a step-by-step overview of the diagnostic process:
- Imaging Tests:
- Chest X-ray: Often the first test to detect abnormalities in the lungs.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the lungs and surrounding tissues.
- PET Scan: Helps determine if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Biopsy:
- A small sample of tissue is taken from the tumor and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
- Laboratory Tests:
- Blood and urine tests may be conducted to check for abnormal hormone levels.
- Molecular Testing:
- This helps identify specific genetic mutations that may influence treatment options.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, the next step is staging the cancer to determine its extent and guide treatment decisions.
Staging Neuroendocrine Lung Cancer
Staging is a critical part of the diagnostic process. It helps doctors understand how far the cancer has spread and plan the most effective treatment strategy. Neuroendocrine lung cancer is typically staged using the TNM system, which evaluates:
- Tumor (T): The size and location of the primary tumor.
- Nodes (N): Whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Metastasis (M): Whether the cancer has spread to distant organs.
Based on these factors, the cancer is assigned a stage from I (early) to IV (advanced). Here’s a simplified breakdown:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Stage I | The tumor is small and confined to the lungs. |
| Stage II | The tumor is larger or has spread to nearby lymph nodes. |
| Stage III | The cancer has spread to more distant lymph nodes or nearby structures. |
| Stage IV | The cancer has spread to distant organs, such as the liver, bones, or brain. |
Understanding the stage of your cancer is crucial for determining the best course of action.
Treatment Options for Neuroendocrine Lung Cancer
Treatment for neuroendocrine lung cancer depends on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. Here are the most common treatment options:
- Surgery:
- Surgery is often the first line of treatment for early-stage neuroendocrine tumors. The goal is to remove the tumor and any affected lymph nodes.
- Radiation Therapy:
- High-energy beams are used to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors. This is often used in combination with other treatments.
- Chemotherapy:
- Chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy cancer cells. It’s commonly used for small cell lung cancer and advanced-stage tumors.
- Targeted Therapy:
- This treatment targets specific genetic mutations or proteins that help cancer cells grow.
- Immunotherapy:
- Immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It’s an emerging treatment option for neuroendocrine lung cancer.
- Somatostatin Analogs:
- These drugs are used to manage symptoms caused by hormone-producing tumors.
Each treatment option has its benefits and risks, so it’s essential to discuss them with your healthcare team to determine the best approach for your situation.
Living with Neuroendocrine Lung Cancer
A diagnosis of neuroendocrine lung cancer can be overwhelming, but there are ways to manage the disease and maintain a good quality of life. Here are some tips:
- Stay Informed: Educate yourself about your condition and treatment options.
- Seek Support: Join support groups or connect with others who are going through a similar experience.
- Follow a Healthy Lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and get enough rest.
- Communicate with Your Healthcare Team: Keep an open line of communication with your doctors and nurses.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. There are resources and professionals available to help you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Neuroendocrine lung cancer is a rare and complex disease that requires a thorough understanding of its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. From recognizing the early signs to exploring the latest therapies, being informed is your greatest ally. While the journey may be challenging, advancements in medical science offer hope for better outcomes and improved quality of life. If you or a loved one is facing this diagnosis, don’t hesitate to seek support and guidance from healthcare professionals. Together, we can navigate the complexities of neuroendocrine lung cancer and work toward a brighter future.
- Neuroendocrine Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Care and Management
- Understanding Neuroendocrine Carcinoid Lung Cancer: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
- Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
- How Does Neuroendocrine Cancer Kill You: Understanding the Silent Threat