Understanding Neuroendocrine Pancreatic Cancer: Symptoms, Treatment, and Hope
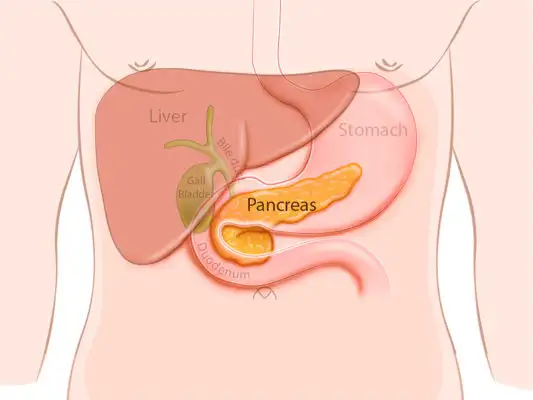
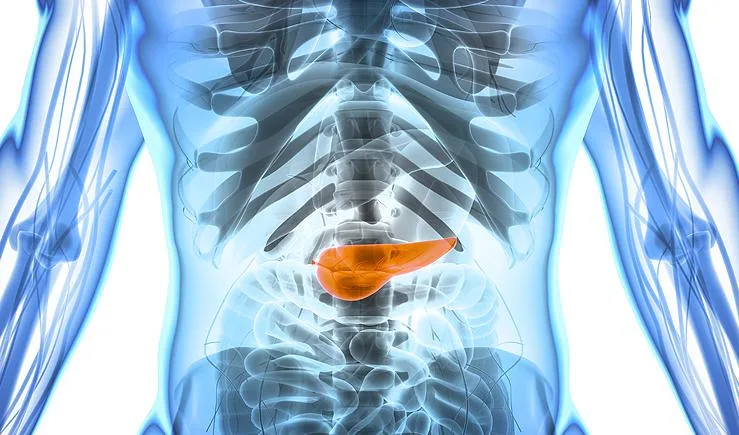
Neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer is a rare but complex form of cancer that originates in the neuroendocrine cells of the pancreas. These cells play a dual role, functioning as both nerve cells and hormone-producing cells, which makes this type of cancer unique in its behavior and treatment. While it accounts for only a small percentage of pancreatic cancers, its impact on patients and their families can be profound.
In this article, we'll dive deep into what neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer is, how it differs from other types of pancreatic cancer, and what treatment options are available. We'll also explore the symptoms, risk factors, and the latest advancements in research that offer hope to those affected. Whether you're a patient, a caregiver, or simply someone looking to learn more, this guide will provide you with clear, actionable information.
What Is Neuroendocrine Pancreatic Cancer?
Neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer, also known as pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs), arises from the neuroendocrine cells in the pancreas. Unlike the more common pancreatic adenocarcinoma, which originates in the exocrine cells, PNETs are often slower-growing and can sometimes be less aggressive. However, this doesn't mean they're any less serious.
These tumors can be functional or non-functional. Functional tumors produce hormones that can cause specific symptoms, such as insulinomas (which produce insulin) or gastrinomas (which produce gastrin). Non-functional tumors, on the other hand, don't produce hormones and may go unnoticed until they grow large enough to cause symptoms like pain or jaundice.
Symptoms of Neuroendocrine Pancreatic Cancer
Recognizing the symptoms of neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer can be challenging because they often mimic other conditions. However, being aware of the signs can lead to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes.
Common Symptoms
- Abdominal pain: A dull ache or sharp pain in the upper abdomen is a frequent complaint.
- Unexplained weight loss: Losing weight without trying can be a red flag.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes may occur if the tumor blocks the bile duct.
- Digestive issues: Nausea, vomiting, or changes in bowel habits can also be signs.
Symptoms Specific to Functional Tumors
- Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar caused by insulinomas can lead to dizziness, confusion, and even fainting.
- Peptic ulcers: Gastrinomas can cause recurrent ulcers in the stomach or small intestine.
- Skin rashes: Glucagonomas may lead to a rash called necrolytic migratory erythema.
If you or a loved one is experiencing any of these symptoms, it's important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Risk Factors and Causes
While the exact cause of neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer is unknown, several risk factors have been identified:
Genetic Factors
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 (MEN1): A hereditary condition that increases the risk of developing neuroendocrine tumors.
- Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome: Another genetic disorder linked to PNETs.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
- Smoking: A known risk factor for many types of cancer, including pancreatic.
- Chronic pancreatitis: Long-term inflammation of the pancreas may increase the risk.
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps to reduce their risk, such as quitting smoking or undergoing genetic testing if there's a family history of related conditions.
Diagnosis and Staging
Diagnosing neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer involves a combination of imaging tests, blood tests, and biopsies.
Diagnostic Tools
- Imaging: CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans can help visualize the tumor.
- Blood and Urine Tests: These can detect abnormal hormone levels.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample is taken to confirm the diagnosis.
Staging
Staging determines how far the cancer has spread and helps guide treatment decisions. The stages range from I (localized) to IV (metastasized).
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Stage I | Tumor is confined to the pancreas. |
| Stage II | Tumor has grown larger or spread to nearby tissues. |
| Stage III | Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. |
| Stage IV | Cancer has metastasized to distant organs. |
Treatment Options
The treatment for neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer depends on the tumor's size, location, and stage, as well as the patient's overall health.
Surgery
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for localized tumors. Procedures may include:
- Whipple procedure: Removal of the head of the pancreas.
- Distal pancreatectomy: Removal of the tail of the pancreas.
Medications
- Somatostatin analogs: These drugs can help control hormone production and slow tumor growth.
- Targeted therapy: Drugs like everolimus and sunitinib target specific pathways in cancer cells.
Radiation and Chemotherapy
These treatments are typically used for advanced cases or when surgery isn't an option.
Emerging Therapies
Clinical trials are exploring new treatments, such as immunotherapy, which harnesses the body's immune system to fight cancer.
Living with Neuroendocrine Pancreatic Cancer
A diagnosis of neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer can be overwhelming, but there are ways to manage the disease and maintain a good quality of life.
Support Systems
- Support groups: Connecting with others who understand your experience can be incredibly comforting.
- Counseling: Professional help can assist in coping with the emotional toll of cancer.
Lifestyle Changes
- Diet: Eating a balanced diet can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
- Exercise: Gentle exercise, like walking or yoga, can boost energy levels and reduce stress.
The Future of Neuroendocrine Pancreatic Cancer Research
Research into neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer is ongoing, with scientists working to better understand the disease and develop more effective treatments. Advances in genetic testing, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy offer hope for improved outcomes in the future.
Conclusion
Neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer is a rare but serious condition that requires careful diagnosis and personalized treatment. By understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and available treatments, patients and their families can make informed decisions and take proactive steps toward managing the disease.
Read more: