Stagescancer.net – Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) is a preventive measure used in cancer treatment to reduce the risk of brain metastases. Brain metastases are tumors that spread to the brain from other parts of the body, and they can have a significant impact on a patient’s quality of life and overall health.
PCI involves the use of radiation therapy to target the brain and prevent the growth of cancer cells that may have spread to this area. This approach has been shown to be effective in reducing the incidence of brain metastases and survival rates in cancer patients.
In this article, we will provide an overview of PCI, its role in cancer treatment, the criteria used to select candidates for this procedure, the different radiation therapy techniques used, the potential benefits and challenges associated with PCI, and the importance of long-term follow-up and patient education.
Key Takeaways
- PCI is a preventive measure used to reduce the risk of brain metastases in cancer patients.
- Brain metastases are tumors that spread to the brain from other parts of the body and can have a significant impact on a patient’s quality of life and overall health.
- PCI involves the use of radiation therapy to target the brain and prevent the growth of cancer cells that may have spread to this area.
- PCI is effective in reducing the incidence of brain metastases and improving overall survival rates in cancer patients.
- The selection of candidates for PCI involves multiple factors, including tumor type and stage.
Understanding Brain Metastases
Brain metastases refer to the spread of cancer cells from other parts of the body to the brain. These malignant tumors can occur in any region of the brain and are classified as secondary brain tumors. Secondary brain tumors are far more common than primary brain tumors, accounting for nearly half of all brain tumor cases.
Brain metastases can arise from a variety of primary cancer types, including lung, breast, colon, and skin cancer. These tumors can have a significant impact on a patient’s overall health, leading to symptoms such as headaches, seizures, and cognitive impairment. The development of brain metastases is a significant complication in cancer treatment.
Preventive measures such as prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) can help reduce the risk of developing brain metastases in cancer patients. Early detection and timely treatment of brain metastases can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Role of Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation in Cancer Treatment
Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) is a widely used treatment strategy for preventing brain metastases in cancer patients. It involves targeting the brain with low-dose radiation therapy after the primary cancer has been treated. PCI aims to eradicate microscopic cancer cells in the brain, making it a valuable tool for cancer treatment.
Research has shown that PCI reduces the incidence of brain metastases in various types of cancer, including small-cell lung cancer and breast cancer. In addition, PCI has been found to improve overall survival in selected patient populations. As a result, PCI is now recommended as a standard of care for certain cancer types.
Cancer Treatment with PCI
| Cancer Type | PCI Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Small Cell Lung Cancer | Standard of care for limited stage disease |
| Breast Cancer | Recommended for high-risk patients |
| Testiculalimited-stage | mended for certain patients with intermediate or high-risk disease |
PCI is typically integrated into comprehensive cancer care plans, which involve collaboration between various healthcare professionals, including oncologists, radiation oncologists, and neurologists. The decision to use PCI is based on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, the patient’s overall health, and the risk of brain metastases.
While PCI has proven to be an effective treatment strategy, it can also have side effects, such as fatigue, headaches, and hair loss. However, the benefits of preventing brain metastases generally outweigh the risks, and many patients find the side effects to be manageable.
Overall, PCI plays a critical role in cancer treatment, helping to prevent brain metastases and improve patient outcomes. As research continues, there is hope for further advancements in PCI techniques and even greater success in treating cancer patients.
Candidate Selection for Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation
Prophylactic cranial irradiation is a treatment aimed at preventing brain metastases in cancer patients. However, not all patients may be suitable candidates for this therapy. Selection criteria may vary depending on tumor types, stage of cancer, and other patient-specific factors that may influence the decision.
In general, prophylactic cranial irradiation is most effective for patients with small-cell lung cancer, who are at high risk of developing brain metastases. For non-small-cell lung cancer, breast cancer, or lymphoma, the decision to undergo prophylactic cranial irradiation may depend on the stage of disease, the presence of specific biomarkers, and other individual factors.
Older patients or those with preexisting conditions, such as neurological disorders, may have a higher risk of developing radiation-related side effects. The patient’s overall health status, treatment preferences, and willingness to undergo prophylactic cranial irradiation should also be considered when selecting candidates.
Ultimately, the decision to offer prophylactic cranial irradiation should be made in consultation with the patient’s oncologist and a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals.
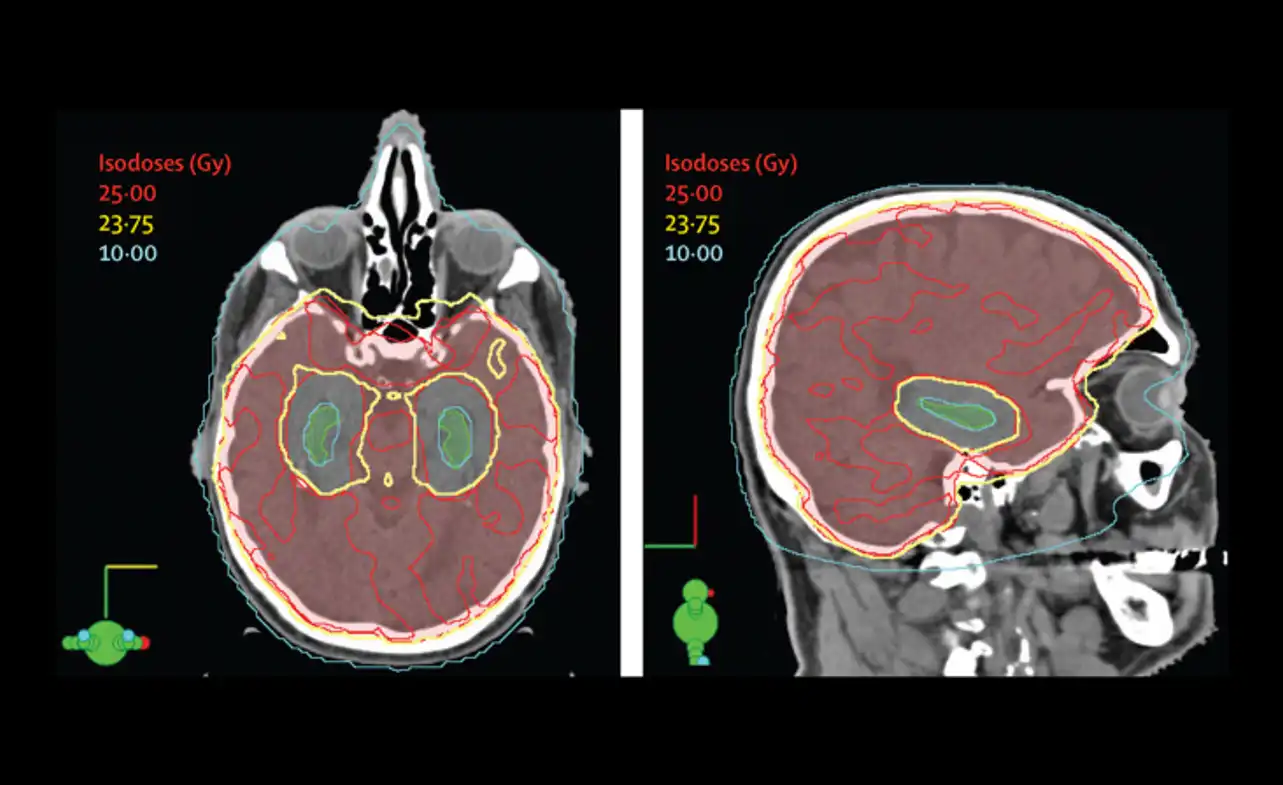
Radiation Therapy Techniques for Preventing Brain Metastases
Radiation therapy is a common strategy for preventing brain metastases in cancer patients. Prophylactic cranial irradiation can be delivered using various techniques, each with its benefits and limitations. The two most commonly used radiation therapy techniques for prophylactic cranial irradiation are:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT) | WBRT delivers radiation to the entire brain, including areas unaffected by the cancer. It is a simple and effective approach to prophylactic cranial irradiation, but it can cause side effects like fatigue, hair loss, and cognitive impairment. |
| Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) | IMRT delivers more precise radiation to the brain, targeting regions most at risk for metastasis. This technique typically produces fewer side effects, but it requires more planning and monitoring to ensure accurate delivery. |
Other radiation therapy techniques that may be used for prophylactic cranial irradiation include stereotactic radiosurgery and hippocampal sparing. These approaches are designed to be even more precise than IMRT, targeting specific areas of the brain while sparing healthy tissue. However, they are still being studied for their effectiveness in preventing brain metastases.
Ultimately, the choice of radiation therapy technique for prophylactic cranial irradiation will depend on various factors, such as the type and stage of cancer, the patient’s overall health, and individualized treatment plans. Consultation with a radiation oncologist is necessary to determine the best approach for each patient.
Benefits of Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation
Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) has several benefits for cancer patients. One of the primary benefits is that it can significantly reduce the risk of brain metastases in patients. Brain metastases can cause a range of neurological symptoms and are associated with poor prognosis for patients. By preventing the spread of cancer cells to the brain, PCI can improve overall survival and increase the quality of life for patients.
In addition to reducing the risk of brain metastases, PCI has other benefits. Studies have shown that it can improve cognitive function in cancer patients, which can be impaired by chemotherapy and other cancer treatments. This can lead to a better quality of life for patients.
However, PCI is not suitable for all cancer patients. The benefits and risks of the treatment depend on various factors, including the type and stage of cancer, as well as the patient’s age and overall health. Optimal candidate selection is necessary to ensure that the benefits of PCI outweigh the potential risks.
| Benefits of Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation | Considerations for Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation |
|---|---|
| Reduced risk of brain metastases | Potential side effects |
| Improved overall survival | Radiation toxicity |
| Increased quality of life | Individualized treatment plans |
| Improved cognitive function | Not suitable for all cancer patients |
Overall, the benefits of prophylactic cranial irradiation outweigh the potential risks for suitable cancer patients. However, it is essential to consider each patient’s unique circumstances and consult with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals before deciding on the treatment.
Considerations and Challenges of Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation
Prophylactic cranial irradiation is a treatment strategy that involves delivering radiation to the brain to prevent or delay the onset of brain metastases in cancer patients. However, like any medical intervention, it has associated considerations and challenges that healthcare providers and patients should be aware of.
Potential Side Effects
One of the main considerations of prophylactic cranial irradiation is the potential for side effects. These can vary depending on the radiation dose and technique used but may include fatigue, scalp irritation, hair loss, headaches, nausea, and cognitive impairment.
It is crucial to discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider before undergoing prophylactic cranial irradiation. They can provide information on how to manage these side effects and improve your overall treatment experience.
Radiation Toxicity
Another consideration is the potential for radiation toxicity. This occurs when radiation damages healthy brain tissue, causing adverse effects. Healthcare providers aim to strike a balance between delivering a therapeutic dose to target cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy brain tissue.
The use of advanced radiation therapy techniques, such as intensity-modulated radiation therapy and stereotactic radiosurgery, can improve the precision and accuracy of radiation delivery, reducing the risk of radiation toxicity.
Individualized Treatment Plans
Prophylactic cranial irradiation is not a one-size-fits-all treatment. The decision to undergo this treatment depends on various factors, such as the patient’s overall health, tumor type and stage, and previous cancer treatments.
It is essential to have a personalized treatment plan that takes into account your unique medical history and circumstances. This allows healthcare providers to optimize the benefits of prophylactic cranial irradiation and minimize the potential risks.
Advances in Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Techniques
Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) has undergone significant advances in recent years, with new techniques being developed to improve treatment outcomes and minimize side effects.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a type of radiation therapy that delivers high-dose radiation directly to the tumor site while sparing normal brain tissue. This approach may be preferred for patients with a limited number of brain metastases, as it offers a more precise and targeted treatment.
Hippocampal Sparing
The hippocampus is a vital brain structure involved in learning and memory. Hippocampal sparing is a technique that aims to minimize radiation exposure to the hippocampus during PCI, reducing the risk of cognitive side effects such as memory loss.
Studies have shown that hippocampal sparing can lead to improved cognitive outcomes in patients undergoing PCI, while still achieving effective control of brain metastases. This technique may be particularly beneficial for patients with a longer life expectancy and those with tumors closer to the hippocampus.
Other Advances
Other advances in PCI techniques include the use of proton therapy and the development of more sophisticated imaging technologies for treatment planning and monitoring. The use of proton therapy may reduce the risk of radiation toxicity to surrounding tissues, while still achieving effective tumor control.
With the continued development of new techniques and technologies, PCI is likely to become even more effective in preventing brain metastases in cancer patients and improving overall treatment outcomes.
Long-term Follow-up and Surveillance After Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation
Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) has been proven effective in preventing brain metastases in cancer patients. However, monitoring is necessary due to potential long-term side effects from radiation exposure and the risk of cancer recurrence.
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to assess the patient’s overall well-being and monitor for any late radiation effects. These appointments should include neurological examinations, imaging tests, and laboratory studies. The frequency of appointments may vary depending on the patient’s risk factors and medical history.
In addition, a team of healthcare professionals should provide close surveillance to detect any recurrence of brain metastases, ensuring that timely treatment can be administered. The use of advanced imaging techniques such as MRI can aid in early detection of tumors. If there is a suspicion of recurrence, biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
It is also important to educate e patients about the potential long-term effects of PCI and the importance of adhering to the follow-up schedule. Patients should be informed about common side effects, such as fatigue, headaches, and cognitive changes, as well as possible rare side effects, such as radiation-induced secondary cancers.
Overall, long-term follow-up and surveillance after prophylactic cranial irradiation is critical to ensure the well-being of cancer patients. Through regular monitoring, potential complications can be detected and treated promptly, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Patient Education and Counseling for Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation
Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) is an important strategy in preventing brain metastases in cancer patients. However, patients must be well-informed about the procedure and receive adequate counseling before making treatment decisions. Patient education and counseling are key components of the shared decision-making process and can help manage expectations, address concerns, and guide patients in making informed choices.
Informed Consent
Before undergoing prophylactic cranial irradiation, patients should be provided with a detailed explanation of the procedure, potential benefits, risks, and side effects. This information should be presented in a clear and understandable manner, using language that is appropriate for the clarification and understandably must also be given ample time to ask questions, clarify doubts, and make a decision based on their values and preferences.
Addressing Concerns
Patients may have concerns about the impact of prophylactic cranial irradiation on their overall health, the potential for side effects, and the effect on their quality of life. These concerns should be addressed in a compassionate and empathetic manner, providing reassurance and information about the benefits and risks of the procedure.
Managing Expectations
Patients should have realistic expectations about the benefits and limitations of prophylactic cranial irradiation. Healthcare providers should provide accurate and evidence-based information about treatment outcomes, including the probability of brain metastases recurrence and the potential risks associated with radiation therapy. This can help prevent misunderstandings, anxiety, and dissatisfaction with treatment outcomes.
Collaborative Care Approach for Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation
Prophylactic cranial irradiation is an essential component of cancer treatment, and the collaborative care approach plays a critical role in managing and supporting patients undergoing this treatment. A multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including radiation oncologists, neuro-oncologists, medical physicists, oncology nurses, and social workers, collaborate to provide comprehensive care to patients.
This approach involves a team-based decision-making process based on individual patient needs and preferences, ensuring that patients receive personalized care and support. This includes initial evaluation and treatment planning, delivery of radiation therapy, management of side effects and symptoms, and long-term follow-up and surveillance.
In addition to medical care, the collaborative care approach also provides patients with emotional, social, and practical support. This includes counseling to address concerns and expectations, education on the treatment process and potential side effects, and financial assistance programs for those who require it.
The Benefits of Collaborative Care Approach for Patients
The collaborative care approach has been shown to improve patient outcomes and satisfaction, reduce treatment-related side effects, and enhance overall quality of life. Research has demonstrated that patients who receive collaborative care experience better treatment adherence, fewer treatment interruptions, and improved symptom control and functioning.
Cost Considerations of Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation
Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) is a significant aspect of cancer treatment, which some patients may need to prevent the spread of cancerous cells to their brains. However, as with most medical treatments, cost is a critical consideration and can add a significant financial burden to patients and their families.
The cost of PCI can vary depending on several factors such as the type of radiation therapy used, the duration of treatment, the availability and location of treatment centers, and insurance coverage. On average, the cost of brain radiation therapy for a cancer patient can range from $8,000 to $23,000 per treatment, leading to a significant financial burden for many individuals and their families.
When the cost of PCI is not covered by their insurance, patients may have to explore alternative payment options, such as financial assistance programs, to make the treatment affordable. For example, some cancer centers offer patient financial assistance programs that can help cover the cost of radiation therapy for eligible patients. Other options include charitable organizations that provide financial support to patients with cancer for treatment-related expenses.
| Radiation Therapy Technique | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|
| Whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT) | $8,000-$12,000 |
| Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) | $14,000-$23,000 |
| Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) | $15,000-$50,000 |
| Hippocampal sparing | $12,000-$18,000 |
It is essential that patients understand the cost implications of prophylactic patients must understand the treatment with their healthcare team. Patients must ask their healthcare team about insurance coverage and other payment options to help mitigate the potential financial burden of the treatment.
Key Takeaways:
- PCI is an essential aspect of cancer treatment for patients at risk of developing brain metastases.
- The cost of PCI may vary depending on the radiation therapy technique used, location of treatment centers, and insurance coverage.
- Patients may explore alternative payment options, such as financial assistance programs, to make the treatment affordable.
- Before undergoing PCI, patients must discuss cost considerations with their healthcare team to make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Patient Experiences and Testimonials
Personal stories and testimonials from cancer patients who have undergone prophylactic cranial irradiation provide valuable insight into their experiences and perspectives. Testimonials are an essential part of patient-centric care, serving as a tool for educating and motivating individuals facing similar health challenges. Patient experiences allow others to understand what to expect, providing a level of comfort and reassurance during an uncertain time.
Janice’s Story
Janice, a 42-year-old mother, was diagnosed with breast cancer that had spread to her lymph nodes. After chemotherapy and mastectomy, she was recommended prophylactic cranial irradiation. Janice was apprehensive about the treatment, having heard about the potential side effects of radiation therapy. However, after undergoing the procedure, Janice reported no major issues, only minor hair loss which she says eventually grew back.
Mark’s Testimonial
Mark, a 58-year-old accountant, was diagnosed with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer that had spread to his liver and brain. After chemotherapsmall-celleted therapy, he underwent prophylactic cranial irradiation. Mark claims that since the treatment he is feeling much better, his symptoms have reduced significantly, and his latest scan showed no sign of any new brain lesions.
These are just two examples of many powerful patient experiences showcasing the benefits of prophylactic cranial irradiation. These stories serve as a reminder of the importance of personalized, holistic cancer care and the positive impact it can have on people’s lives.
Research and Future Perspectives on Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation
Current research on prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) continues to show promising results in preventing brain metastases in cancer patients. Ongoing studies aim to refine and optimize current treatment protocols, while embracing emerging technology such as intensity-modulated radiotherapy, hippocampal sparing, and technology radiosurgery.
In addition to optimizing treatment strategies, research is also focusing on improving patient selection criteria for prophylactic cranial irradiation. This includes developing more accurate prognostic models and biomarkers that can help identify patients most likely to benefit from PCI, while minimizing the risk of treatment-related side effects.
Looking to the future, researchers are exploring the potential for combining PCI with other novel therapies such as immunotherapy and targeted molecular therapies. These approaches seek to leverage the synergistic effects of multiple treatment modalities to enhance outcomes and reduce toxicity.
Ongoing Studies and Emerging Trends in PCI Research
| Study or Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) | A form of radiation therapy that allows for precise targeting of cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy surrounding tissue. Ongoing studies aim to refine IMRT protocols for use in prophylactic cranial irradiation. |
| Hippocampal sparing | A radiation therapy technique that delivers targeted treatments to the brain while minimizing radiation exposure to the hippocampus, a region of the brain essential to memory function. Emerging research suggests hippocampal sparing may reduce cognitive side effects associated with prophylactic cranial irradiation. |
| Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) | A non-invasive radiation therapy technique that delivers targeted radiation to small, well-defined areas of the brain. Ongoing studies aim to investigate the safety and efficacy of SRS in the context of prophylactic cranial irradiation. |
| Combination therapy | Emerging research suggests that combining prophylactic cranial irradiation with other treatment modalities such as immunotherapy and targeted molecular therapies may enhance treatment response and improve patient outcomes. |
Overall, the future of prophylactic cranial irradiation looks promising, with ongoing research and technological advancements paving the way for improved treatment outcomes and quality of life for cancer patients.
Conclusion and Takeaways
Prophylactic cranial irradiation is a valuable treatment strategy that can prevent brain metastases and improve overall survival for cancer patients. As discussed in this article, selecting the right candidates, using appropriate radiation therapy techniques, and providing long-term monitoring and supportive care are essential for successful treatment outcomes.
Despite the potential benefits, prophylactic cranial irradiation may not be suitable for every patient and may have certain challenges and considerations. As a result, patient education and counseling, as well as a collaborative care approach involving a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, are crucial for making informed decisions and managing patient expectations.
It is essential to note that the cost of prophylactic cranial irradiation can vary depending on several factors, including insurance coverage and potential financial assistance programs. Patients should consult with their healthcare providers and insurance companies to understand the cost implications and available resources.
In conclusion, prophylactic cranial irradiation represents a significant advance in cancer treatment that can benefit patients at risk of brain metastases. By staying informed, working collaboratively with healthcare professionals, and keeping an open mind, patients can make empowered decisions about their care and achieve better outcomes.
FAQ
What is prophylactic cranial irradiation?
Prophylactic cranial irradiation is a treatment technique used to prevent brain metastases in cancer patients. It involves the use of radiation therapy to target and reduce the risk of cancer cells spreading to the brain.
What are brain metastases?
Brain metastases refer to secondary tumors that occur in the brain as a result of cancer cells spreading from another part of the body. They can impact the overall health and well-being of cancer patients.
How does prophylactic cranial irradiation fit into cancer treatment?
Prophylactic cranial irradiation plays a crucial role in cancer treatment by helping to prevent the development of brain metastases. It is often integrated into comprehensive care plans for certain types and stages of cancer.
How are candidates selected for prophylactic cranial irradiation?
Candidate selection for prophylactic cranial irradiation is based on various factors, including the type of tumor, stage of cancer, and the overall health of the patient. Decisions are made by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals.
What are the different radiation therapy techniques used in prophylactic cranial irradiation?
Prophylactic cranial irradiation can be delivered through various radiation therapy techniques, including whole-brain radiation therapy and intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Each technique has its benefits and limitations.
What are the benefits of prophylactic cranial irradiation?
Prophylactic cranial irradiation offers several benefits, such as reducing the risk of brain metastases, improving overall survival rates in cancer patients, and enhancing their quality of life by preventing neurological complications.
What considerations and challenges are associated with prophylactic cranial irradiation?
There are several considerations and challenges to consider with prophylactic cranial irradiation, including potential side effects of radiation therapy, radiation toxicity, and the need for individualized treatment plans based on patient-specific factors.
Are there any advances in prophylactic cranial irradiation techniques?
Yes, there have been recent advances in prophylactic cranial irradiation techniques, such as stereotactic radiosurgery and hippocampal sparing. These advancements aim to improve treatment outcomes and minimize side effects.
Why is long-term follow-up and surveillance important after prophylactic cranial irradiation?
Long-term follow-up and surveillance after prophylactic cranial irradiation are important to monitor for late radiation effects, recurrence of brain metastases, and overall patient well-being. Regular check-ups and imaging tests may be recommended.
How does patient education and counseling play a role in prophylactic cranial irradiation?
Patient education and counseling are vital in ensuring informed consent, addressing patient concerns, and managing expectations regarding prophylactic cranial irradiation. It helps patients make well-informed decisions about their treatment.
What is the collaborative care approach for patients undergoing prophylactic cranial irradiation?
The collaborative care approach involves a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals working together to manage and support cancer patients undergoing prophylactic cranial irradiation. This ensures comprehensive care and improved treatment outcomes.
Are there cost considerations associated with prophylactic cranial irradiation?
Yes, there are cost considerations to take into account with prophylactic cranial irradiation. These include treatment expenses, insurance coverage, and potential financial assistance programs that may help alleviate some of the financial burden.
What do patient experiences and testimonials reveal about prophylactic cranial irradiation?
Patient experiences and testimonials provide valuable insights into the impact of prophylactic cranial irradiation on their lives. They offer firsthand accounts of the treatment process, its effects, and the overall benefits and challenges faced.
What is the current research and future perspectives on prophylactic cranial irradiation?
Ongoing research focuses on improving prophylactic cranial irradiation techniques, exploring advancements in technology such as stereotactic radiosurgery, and identifying new approaches to enhance treatment outcomes and minimize side effects.
What are the key takeaways from the article on prophylactic cranial irradiation?
The key takeaways from this article include the benefits of prophylactic cranial irradiation in preventing brain metastases, the importance of patient education and counseling, the collaborative care approach for managing cancer patients, and the ongoing research and advancements in this field.