Stagescancer.net – When undergoing treatment for lung cancer, patients may be recommended brain radiation as part of their therapy. While this approach can be effective in targeting cancer cells in the brain, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects that may accompany this treatment. Understanding these side effects is crucial for patients and their loved ones to prepare and manage the challenges that may arise.
In this article, we will explore the common side effects of brain radiation for lung cancer. From cognitive impairment and fatigue to hair loss and nausea, we will delve into the physical and emotional impact that patients may experience during and after treatment. Additionally, we will provide practical tips and strategies for managing these side effects and discuss the importance of open communication with your healthcare team.
It is essential to remember that each patient’s experience with brain radiation may vary. This article aims to shed light on what to expect and equip patients with the knowledge to navigate their treatment journey with confidence. Let’s dive into the side effects of brain radiation for lung cancer and explore ways to mitigate their impact.
What is Brain Radiation for Lung Cancer?
Brain radiation treatment plays a crucial role in the comprehensive management of lung cancer. It is a form of radiotherapy that targets cancer cells in the brain, helping to control tumor growth and improve overall prognosis for patients. Administered using precise techniques, this treatment aims to deliver high doses of radiation to the tumor while minimizing exposure to healthy surrounding tissues.
During brain radiation for lung cancer, powerful beams of radiation are directed at the tumor site. This targeted approach allows for the destruction of cancer cells and inhibits their ability to multiply. By shrinking or controlling the growth of brain metastases, brain radiation treatment can alleviate symptoms and enhance a patient’s quality of life.
It is important to note that brain radiation is often used in conjunction with other treatments, such as surgery and chemotherapy, to form a comprehensive lung cancer treatment plan. This multi-modal approach helps to address both local and systemic diseases, improving the chances of successful outcomes.
How is Brain Radiation for Lung Cancer Administered?
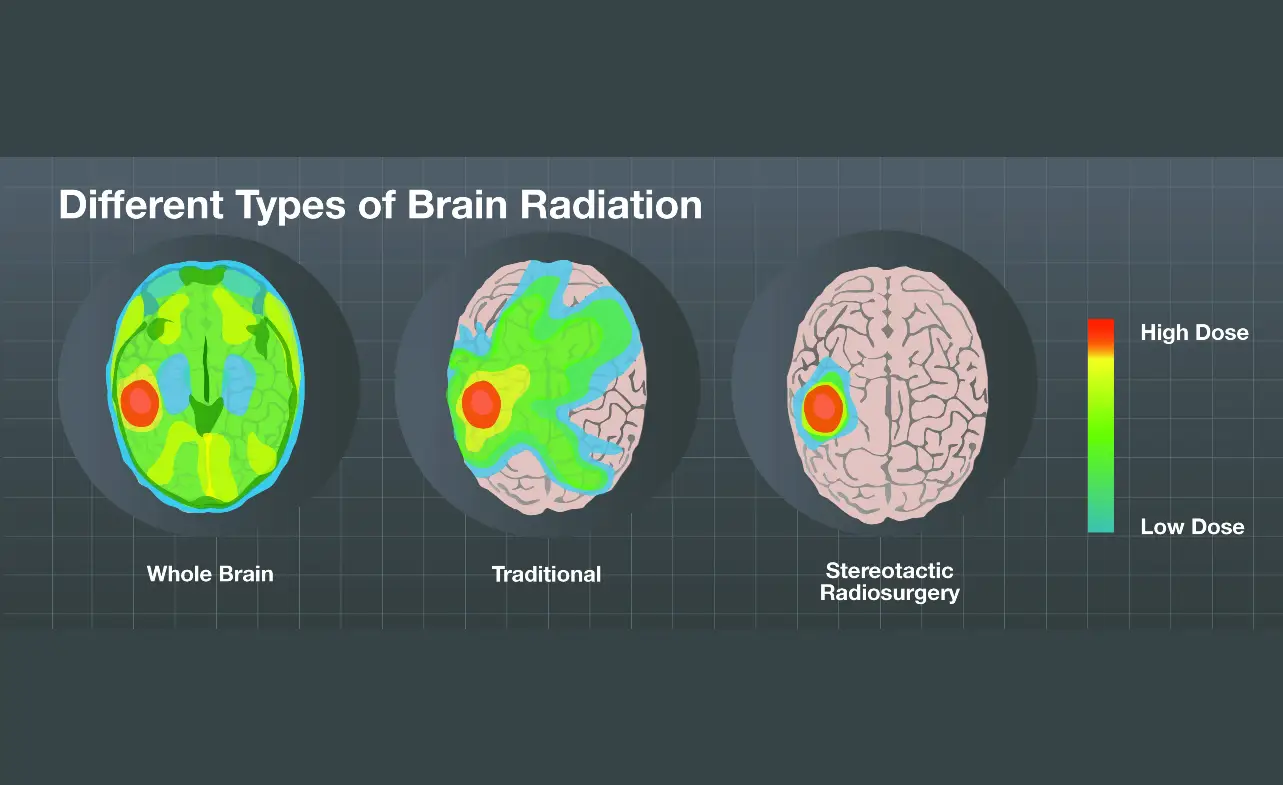
Brain radiation treatment can be delivered through different methods depending on the size, location, and number of brain metastases. The two primary techniques used are:
- Whole Brain Radiation Therapy (WBRT): In this approach, radiation is delivered to the entire brain. It is commonly used in cases where multiple brain metastases are present or when cancer has spread extensively within the brain.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS): SRS is a highly precise form of radiation therapy that delivers focused radiation beams directly to the tumor site. This technique allows for maximum control and minimal damage to healthy surrounding tissues. SRS is often used when there are fewer brain metastases or when tumors are located in critical areas of the brain.
The choice of radiation technique depends on various factors, including the patient’s overall health, the size and number of brain metastases, and individual treatment goals. The healthcare team, including radiation oncologists and neurosurgeons, will assess these factors and determine the most appropriate approach for each patient.
Now that we have explored what brain radiation treatment entails for lung cancer patients, let’s delve into the common side effects that can arise as a result of this therapy.
Common Side Effects of Brain Radiation
When undergoing brain radiation as part of lung cancer treatment, patients may experience a range of common side effects. These side effects can vary in severity and duration, impacting the physical and emotional well-being of individuals. Patients need to be aware of these potential side effects and work closely with their healthcare team to manage them effectively.
Short-Term Side Effects
Short-term side effects of brain radiation treatment for lung cancer can occur during or shortly after the radiation sessions. These may include:
- Fatigue: Many patients report feeling tired or experiencing a lack of energy.
- Headaches: Some individuals may experience headaches, ranging from mild to more severe.
- Nausea and vomiting: These side effects can occur, but can often be controlled with medications.
Long-Term Side Effects
In addition to short-term side effects, there are potential long-term effects of brain radiation for lung cancer. These effects may develop months or even years after treatment and can include:
- Cognitive impairment: Brain radiation can affect memory, thinking, and concentration abilities.
- Hair loss: Temporary hair loss may occur in the treatment area.
- Swelling and edema: Radiation can cause swelling in the brain, leading to potential complications.
Patients need to discuss any side effects they experience with their healthcare team. Medical professionals can provide appropriate guidance and support to help manage and mitigate these side effects.
| Side Effect | Description | Treatment and Management |
|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Feeling tired or lacking energy | Managing daily activities, resting when needed, and incorporating gentle exercise |
| Headaches | Pain or discomfort in the head | Over-the-counter pain relievers, applying cold or warm compresses, staying hydrated |
| Nausea and vomiting | The feeling of sickness and vomiting | Prescribed anti-nausea medications, eating small meals, avoiding triggering foods |
| Cognitive impairment | Changes in memory, thinking, and concentration abilities | Memory exercises, cognitive therapy, seeking support from healthcare professionals |
| Hair loss | Temporary loss of hair in the treatment area | Using head coverings, such as hats or scarves, and discussing potential regrowth options |
| Swelling and edema | The build-up of fluid causes swelling in the brain | Medications to reduce swelling, lifestyle modifications, close monitoring by healthcare team |
Cognitive Impairment
One of the significant side effects associated with brain radiation for lung cancer is cognitive impairment. This condition refers to changes in memory, thinking abilities, and overall cognitive function. Patients undergoing brain radiation may experience difficulties with recall, concentration, and problem-solving.
The cognitive impairment caused by brain radiation can vary in severity and duration. Some patients may only experience temporary difficulties, while others may face long-term challenges in their cognitive abilities.
It is essential to understand that the specific impact of cognitive impairment can vary from person to person. Factors such as the individual’s age, overall health, and radiation dosage can influence the severity and duration of cognitive changes.
The Effects on Memory and Thinking Abilities:
Cognitive impairment can affect various aspects of memory and thinking abilities, including:
- Short-term memory loss
- Difficulty multitasking
- Slower processing speed
- Trouble concentrating
- Decreased attention span
These effects can significantly impact a patient’s daily life, making it challenging to perform regular tasks, work, or engage in social interactions.
Managing Cognitive Impairment:
While cognitive impairment can pose challenges, some strategies and techniques can help patients cope with these changes. Some approaches include:
- Engaging in cognitive exercises and brain training activities
- Practicing good sleep hygiene to enhance cognitive function
- Implementing organizational strategies to improve memory and task management
- Seeking support from healthcare professionals, such as occupational therapists or cognitive rehabilitation specialists
By incorporating these strategies into their daily lives, patients can optimize their cognitive function and improve their overall quality of life.
| Common Cognitive Impairment Symptoms | Management Strategies |
|---|---|
| Short-term memory loss | Engaging in memory exercises and techniques |
| Difficulty multitasking | Breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps |
| Slower processing speed | Allowing extra time for completing tasks |
| Trouble concentrating | Practicing mindfulness and meditation techniques |
| Decreased attention span | Minimizing distractions and creating a focused work environment |
Fatigue and Weakness
Patients undergoing brain radiation for lung cancer often experience fatigue and weakness as side effects of the treatment. These symptoms can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life and daily functioning. Understanding the severity of these symptoms and implementing effective management strategies is crucial for patients undergoing brain radiation treatment.
Severity of Fatigue and Weakness
Fatigue and weakness can vary in intensity from mild to severe, depending on individual factors such as the dosage and duration of brain radiation treatment. Some patients may experience occasional fatigue and weakness, while others may have persistent and debilitating symptoms. Patients and healthcare providers need to communicate openly about the severity of these symptoms to ensure appropriate support and management strategies are implemented.
Managing Fatigue and Weakness
There are various strategies that patients can employ to manage fatigue and weakness during and after brain radiation treatment:
- Conserve Energy: Prioritize activities and allocate energy levels accordingly. Pace yourself throughout the day and take frequent rest breaks to prevent excessive fatigue.
- Exercise: Engage in gentle exercises such as walking or stretching, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, to improve energy levels and maintain muscle strength.
- Optimize Sleep: Ensure a restful sleep routine by maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques before bedtime.
- Nutrition: Eat a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods to support energy levels and overall health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to prevent dehydration, which can contribute to fatigue.
- Supportive Care: Seek support from healthcare professionals or support groups who can provide guidance and emotional support during the treatment journey.
Management Strategies for Fatigue and Weakness
| Management Strategies | Description |
|---|---|
| Conserve Energy | Prioritize activities and allocate energy levels accordingly. Pace yourself throughout the day and take frequent rest breaks to prevent excessive fatigue. |
| Exercise | Engage in gentle exercises such as walking or stretching, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, to improve energy levels and maintain muscle strength. |
| Optimize Sleep | Ensure a restful sleep routine by maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques before bedtime. |
| Nutrition | Eat a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods to support energy levels and overall health. |
| Stay Hydrated | Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to prevent dehydration, which can contribute to fatigue. |
| Supportive Care | Seek support from healthcare professionals or support groups who can provide guidance and emotional support during the treatment journey. |
Hair Loss
One of the temporary side effects experienced by lung cancer patients undergoing brain radiation is hair loss. Although it can be distressing and emotionally challenging, it is important to understand that hair loss is a common occurrence during radiation treatment.
This side effect arises due to the impact of radiation on hair follicles, leading to the temporary cessation of hair growth. The extent and duration of hair loss can vary from person to person, with some individuals experiencing only partial hair loss while others may lose all their hair.
Healthcare providers need to discuss the possibility of hair loss with patients before starting radiation treatment. Providing accurate information and addressing concerns can help patients psychologically prepare for this change in their appearance.
While hair loss during radiation treatment is temporary, it may take several weeks or months for hair to grow back after completing the treatment. The regrowth rate and pattern can vary, but most patients witness gradual improvement over time.
Emotional Impact of Hair Loss
The emotional impact of hair loss can be significant for lung cancer patients undergoing brain radiation. It is normal to experience a range of emotions, including sadness, frustration, and a loss of confidence. Dealing with these emotions is an important aspect of the overall treatment journey.
Supportive healthcare professionals, such as oncologists and nurses, play a crucial role in addressing the emotional aspect of hair loss. By providing empathy, understanding, and resources for emotional support, they help patients navigate this challenging period with resilience and self-acceptance.
Coping Strategies and Support
There are various coping strategies and support resources available to help lung cancer patients manage hair loss during radiation treatment. Some options include:
- Wearing hats, scarves, or wigs to cover the head
- Exploring different hair accessories and styling options
- Connecting with support groups for mutual understanding and guidance
- Seeking counseling or therapy services to process emotional concerns
- Utilizing scalp cooling treatments to potentially reduce the severity of hair loss
Patients need to communicate openly with their healthcare team about their concerns and preferences regarding hair loss. By working together, patients and healthcare professionals can develop personalized strategies to address the emotional impact and enhance overall well-being.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Temporary side effect | Emotionally challenging |
| A normal part of radiation treatment | Loss of confidence |
| Opportunity for self-expression through head coverings | Gradual regrowth process |
| Availability of coping strategies and support resources | Individual experiences may vary |
Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are common side effects experienced by patients undergoing brain radiation treatment for lung cancer. These symptoms can be distressing and affect a patient’s overall well-being. In this section, we will delve into the possible causes of nausea and vomiting, provide strategies for prevention, and discuss effective medications to alleviate these symptoms.
Possible Causes of Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting can be triggered by various factors related to brain radiation treatment. These may include:
- The direct effect of radiation on the brain affects the region responsible for regulating nausea and vomiting.
- Irregularities in the gastrointestinal system due to radiation exposure.
- Anxiety and stress associated with the treatment process.
Prevention Strategies
To minimize the occurrence of nausea and vomiting during brain radiation treatment, patients can consider implementing the following strategies:
- Eating smaller, frequent meals throughout the day instead of larger ones.
- Avoid foods and smells that trigger nausea.
- Staying hydrated by drinking enough fluids.
- Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, to reduce stress and anxiety.
Medications for Alleviating Nausea and Vomiting
If nausea and vomiting persist despite preventive measures, healthcare providers may prescribe medications known as antiemetics. These medications can help relieve these symptoms and improve a patient’s quality of life. Commonly prescribed antiemetics include:
- Ondansetron (Zofran)
- Prochlorperazine (Compazine)
- Metoclopramide (Reglan)
- Aprepitant (Emend)
Patients need to communicate any side effects they experience to their healthcare team, as adjustments to the treatment plan and supportive care strategies can be implemented to enhance their comfort and well-being.
Headaches and Migraines
Headaches and migraines are common side effects of brain radiation treatment for lung cancer. These symptoms can be distressing and have a significant impact on a patient’s quality of life. Understanding the causes, duration, and intensity of these headaches and migraines is essential in managing them effectively.
Causes
The exact cause of headaches and migraines following brain radiation treatment is not fully understood. However, it is believed that radiation can affect blood vessels in the brain, leading to inflammation and increased sensitivity to pain. Additionally, changes in brain chemistry and nerve function may contribute to these symptoms.
Duration and Intensity
The duration and intensity of headaches and migraines can vary among individuals. Some patients may experience occasional mild headaches, while others may have frequent and severe migraines. These symptoms can persist for weeks or months after completing radiation treatment.
Management Strategies
Managing headaches and migraines requires a comprehensive approach that combines medication, lifestyle modifications, and alternative therapies. The following strategies may be helpful:
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications may help alleviate headaches and migraines. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
- Stress management: Stress can exacerbate headaches and migraines. Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress levels.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial in preventing and managing headaches. Aim to drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day.
- Rest and sleep: Sufficient rest and quality sleep are important for headache and migraine management. Establishing a regular sleep routine and creating a sleep-friendly environment can be beneficial.
- Dietary adjustments: Certain foods and beverages, such as caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods, may trigger headaches and migraines. Keeping a food diary and avoiding known triggers can help identify and manage these triggers effectively.
- Complementary therapies: Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, biofeedback, and massage, may provide relief for some individuals. It is recommended to consult with healthcare professionals experienced in these therapies.
Patients must communicate their symptoms and experiences with their healthcare team to ensure appropriate management and support.
| Management Strategies | Description |
|---|---|
| Medication | Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications may help alleviate headaches and migraines. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advised for proper evaluation and guidance. |
| Stress management | Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress levels and minimize the frequency and intensity of headaches and migraines. |
| Hydration | Staying hydrated is crucial in preventing and managing headaches. Ensuring adequate water intake throughout the day is recommended. |
| Rest and sleep | Sufficient rest and quality sleep are important for headache and migraine management. Establishing a regular sleep routine and creating a sleep-friendly environment can be beneficial. |
| Dietary adjustments | Avoiding known triggers such as caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods can help manage headaches and migraines. Keeping a food diary can assist in identifying triggers. |
| Complementary therapies | Alternative therapies like acupuncture, biofeedback, and massage may provide relief for some individuals. Consultation with healthcare professionals experienced in these treatments is recommended. |
Swelling and Edema
One of the potential side effects of brain radiation treatment for lung cancer is swelling and edema in the brain. Swelling refers to an abnormal enlargement of tissues caused by an accumulation of fluid, while edema refers to the excess fluid retention in the body’s tissues. In the context of brain radiation, swelling, and edema can specifically occur in the brain due to the treatment’s effects on the surrounding tissues.
This side effect can cause discomfort and impact the normal functioning of the brain. It may lead to symptoms such as headaches, nausea, and changes in mood or behavior. In severe cases, it can also result in neurological deficits.
Risks and Management Strategies
Healthcare providers need to monitor and manage swelling and edema during and after brain radiation treatment. The potential risks associated with these side effects include increased intracranial pressure, compromised blood flow to the brain, and exacerbation of pre-existing conditions.
To manage swelling and edema effectively, various strategies can be implemented:
- Medications: Your healthcare team may prescribe corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and decrease swelling. Diuretics can also be used to help eliminate excess fluid from the body.
- Elevating the head: Sleeping or resting with the head slightly elevated can help alleviate symptoms by reducing fluid accumulation in the brain.
- Dietary adjustments: Reducing sodium intake can aid in reducing fluid retention.
- Monitoring: Regular imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, may be conducted to assess the extent of swelling and edema and guide the appropriate management.
Patients must communicate any changes in symptoms or discomfort to their healthcare team promptly. Through effective management and continuous monitoring, healthcare providers can ensure the well-being of patients undergoing brain radiation treatment for lung cancer.
| Side Effect | Management Strategies |
|---|---|
| Swelling and Edema |
|
Difficulty Swallowing and Eating
During brain radiation treatment for lung cancer, patients may experience difficulty swallowing and eating, which can significantly impact their nutrition and overall well-being. This section aims to provide insights into the causes of these challenges and offer strategies to overcome them.
Causes of Difficulty Swallowing and Eating
Difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia, may occur due to the radiation’s impact on the muscles and tissues in the throat and esophagus. The radiation can cause inflammation, scarring, and narrowing, making it challenging for food and liquids to pass through comfortably.
Additionally, brain radiation can affect the sense of taste and smell, leading to changes in appetite and enjoyment of food. It may also cause a dry mouth, making it harder to chew and swallow without sufficient saliva.
Impact on Nutrition
Difficulty swallowing and eating can have severe implications for a patient’s nutrition and overall health. Insufficient food intake can result in weight loss, malnutrition, and decreased energy levels. These factors can hamper the body’s ability to recover from treatment and may affect the success of the overall lung cancer management plan.
Furthermore, the frustration and discomfort associated with difficulty swallowing can contribute to emotional distress and reduced quality of life.
Strategies to Overcome Difficulty Swallowing and Eating
While the challenges of difficulty swallowing and eating can feel overwhelming, some approaches and strategies can help patients manage these symptoms effectively. Here are some practical tips:
- Consult with a dietitian who specializes in oncology nutrition to develop a personalized meal plan that ensures adequate nutrition while considering restrictions related to swallowing difficulties.
- Modify food consistency: Adjusting the texture of foods can make them easier to swallow. For example, pureeing or blending solid foods or choosing softer options can help minimize swallowing challenges.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids throughout the day can help lubricate the throat and ease swallowing discomfort. Sipping water or using saliva substitutes may be beneficial.
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals: Opting for smaller, more frequent meals instead of large portions can make swallowing easier and reduce the feeling of fullness.
- Take breaks and eat slowly: Eating at a relaxed pace and taking breaks between bites can help manage swallowing difficulties. It’s essential to chew food thoroughly to aid digestion.
- Consider specialized swallowing techniques: Speech therapists can guide techniques such as swallowing exercises and postures that assist in overcoming swallowing difficulties.
In some cases, healthcare professionals may recommend a temporary feeding tube to ensure adequate nutrition until swallowing difficulties improve.
| Food and Beverage Recommendations | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Soft, pureed foods | Easier to swallow and requires less effort to chew |
| Smoothies and milkshakes | Provides essential nutrients in a liquid form |
| Soups and broths | Easily consumed and helps maintain hydration |
| Moist and tender meats | Can be easier to swallow compared to tougher cuts |
| Soft fruits and vegetables | Provides vitamins, fiber, and hydration |
Emotional and Psychological Effects
Brain radiation for lung cancer can have profound emotional and psychological effects on patients. The journey of receiving treatment and dealing with its side effects can be overwhelming, leading to various challenges in mental well-being. It’s essential to acknowledge and address these effects to provide comprehensive care and support to patients.
The Impact on Mental Health
The emotional effects of brain radiation can manifest differently in each individual. Patients may experience heightened levels of anxiety, stress, depression, and fear throughout their treatment journey. The uncertainty surrounding the outcomes and potential long-term effects can contribute to these feelings.
Healthcare providers must assess and monitor the mental health of patients receiving brain radiation. By offering appropriate support and interventions, healthcare teams can help patients navigate these challenges and promote better overall well-being.
Coping Mechanisms and Support Resources
Developing effective coping mechanisms is essential for patients undergoing brain radiation. It’s crucial to encourage patients to seek emotional support from their loved ones, as well as professional counselors or support groups. These resources can provide a safe space for patients to express their emotions, share experiences, and learn from others facing similar challenges.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness-based techniques are also beneficial in helping patients manage stress and anxiety. These therapeutic approaches can empower individuals to develop resilience and enhance their emotional well-being throughout the treatment process.
Support organizations such as the American Cancer Society and Lung Cancer Foundation offer educational resources, helplines, and support networks specifically tailored for lung cancer patients. These resources provide valuable information, guidance, and emotional support throughout the treatment journey.
The Importance of Comprehensive Care
Recognizing and addressing the emotional and psychological effects of brain radiation is a crucial aspect of comprehensive care for lung cancer patients. By integrating mental health support into the treatment plan, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes, enhance their quality of life, and promote overall well-being.
| Emotional Effects | Psychological Effects |
|---|---|
| Heightened anxiety | Depression |
| Elevated stress levels | Fear and uncertainty |
| Decreased quality of life | Changes in self-perception |
Long-Term Effects and Survivorship
Brain radiation treatment can have significant long-term effects on lung cancer survivors. It is essential to understand the potential risks and complications that may arise following treatment and the importance of long-term follow-up care.
Potential Risks and Complications
While brain radiation is crucial in treating lung cancer, it can lead to several long-term effects. These effects may vary depending on various factors, such as the radiation dose received and the individual’s overall health. Common long-term effects of brain radiation include:
- Memory and cognitive impairment
- Motor and coordination difficulties
- Hearing and vision problems
- Hormonal imbalances
- Increased risk of secondary cancers
- Psychological and emotional challenges
Importance of Long-Term Follow-Up Care
Given the potential long-term effects, it is crucial for lung cancer survivors who have undergone brain radiation to receive regular follow-up care. This care aims to monitor for any late-onset side effects, address ongoing concerns and complications, and provide necessary support for survivorship.
Long-term follow-up care may include:
- Regular medical check-ups and imaging
- Cognitive and neuropsychological assessments
- Hormone level monitoring
- Hearing and vision evaluations
- Mental health support and counseling
- Cancer survivorship programs
By participating in long-term follow-up care, lung cancer survivors can proactively manage potential complications and receive appropriate interventions to enhance their quality of life.
Managing Side Effects
When undergoing brain radiation for lung cancer, managing the side effects is an essential aspect of the treatment journey. While side effects can vary from person to person, some several practical strategies and therapies can help alleviate discomfort and improve overall well-being. From lifestyle adjustments to complementary therapies, exploring different approaches can make a significant difference in managing side effects and enhancing quality of life.
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting certain lifestyle changes can help minimize the impact of side effects. These may include:
- Following a well-balanced diet supports the body’s nutritional needs and promotes healing.
- Engaging in regular exercise to maintain physical strength and mental well-being.
- Getting sufficient rest and managing stress levels through relaxation techniques.
- Quitting smoking and avoiding alcohol, can exacerbate side effects and hinder the healing process.
Complementary Therapies
Complementary therapies have shown promise in managing side effects and improving overall well-being during lung cancer treatment. Some examples include:
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese therapy involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to help alleviate pain, nausea, and fatigue.
- Massage Therapy: Massage can help reduce muscle tension, improve relaxation, and provide relief from pain and fatigue.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Practices such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress, improve sleep quality, and enhance overall mental well-being.
- Herbal Supplements: Some herbal supplements, such as ginger or ginseng, may help manage specific side effects. However, it is important to consult with healthcare professionals before incorporating any supplements into the treatment regimen.
Discussion and Support
Open and honest communication with the healthcare team is crucial for effectively managing side effects. Regular discussions with healthcare professionals can help address concerns, modify treatment plans if necessary, and provide guidance on self-care practices. Support from family, friends, and cancer support groups can also be invaluable, offering emotional and practical support throughout the treatment process.
Communicating with Your Healthcare Team
Effective communication plays a vital role in your journey through brain radiation treatment for lung cancer. Building a strong and collaborative relationship with your healthcare team is essential to address any side effects or concerns that may arise.
Open dialogue and transparent communication with your healthcare team allow you to:
- Discuss your treatment goals and expectations
- Share your concerns about side effects
- Ask questions about the treatment process
- Express any discomfort or pain you may experience
- Receive timely information and updates about your condition
Your healthcare team, consisting of doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals, is experienced in managing the side effects of brain radiation. They are there to support and guide you every step of the way. By effectively communicating your needs, you can work together to develop a personalized care plan to minimize any potential side effects and maximize the effectiveness of your treatment.
Here are a few tips for effective communication with your healthcare team during brain radiation treatment:
- Be prepared: Write down any questions or concerns you may have before your appointments. This will help you remember everything you want to discuss.
- Be honest: Share your symptoms and side effects openly and honestly with your healthcare team. Providing accurate information will help them assess your condition and adjust your treatment plan if necessary.
- Take notes: During your appointments, jot down important information, instructions, and any changes in your treatment plan. This will help you remember and follow any recommended guidelines.
- Ask for explanations: If there is something you don’t understand, don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare team for clarification. They are there to educate and guide you through your treatment.
- Seek support: If you are feeling overwhelmed or experiencing emotional distress, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare team. They can provide resources and support to address your psychological well-being.
Remember, effective communication fosters a trusting relationship between you and your healthcare team, ensuring the best possible care during your brain radiation treatment for lung cancer.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have explored the side effects of brain radiation for lung cancer treatment. It is essential to understand that while brain radiation can be an effective treatment option, it can also have various side effects that may impact a patient’s quality of life.
From cognitive impairment and fatigue to hair loss and nausea, patients may experience a range of physical and emotional challenges during and after treatment. However, it is crucial to note that not all individuals will experience the same side effects, and the severity can vary.
Managing these side effects requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates effective communication with healthcare teams, individualized care plans, and ongoing support. Patients need to communicate openly with their healthcare providers and seek guidance to alleviate symptoms and enhance their well-being.
During this journey, patients should focus on self-care, adhere to lifestyle adjustments, and explore complementary therapies to address their specific side effects. Additionally, understanding the long-term effects and survivorship is crucial, emphasizing the need for continuous follow-up care and monitoring.
In conclusion, while the side effects of brain radiation for lung cancer treatment can be challenging, it is essential to emphasize the importance of providing adequate support, tailored care, and open communication in addressing these side effects. By working closely with their healthcare team, patients can navigate the side effects, minimize their impact, and improve their overall treatment experience.
FAQ
What is brain radiation for lung cancer?
Brain radiation for lung cancer is a treatment that involves targeting and delivering high-energy X-rays or protons to the brain to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors. It is often used when lung cancer has spread to the brain or as a preventive measure when there is a high risk of metastasis.
What are the common side effects of brain radiation?
Common side effects of brain radiation for lung cancer include fatigue, hair loss, nausea, vomiting, headaches, and cognitive impairment. These side effects can vary in severity and may occur during or after treatment. It is important to communicate with your healthcare team about any symptoms experienced.
How does brain radiation affect cognitive function?
Brain radiation can lead to cognitive impairment, which may affect memory, concentration, and overall cognitive function. The extent and duration of cognitive changes can vary among individuals. It is important to discuss any cognitive difficulties with your healthcare team to develop appropriate management strategies.
What can be done to manage fatigue and weakness during brain radiation treatment?
To manage fatigue and weakness during brain radiation treatment, it is important to prioritize rest and conserve energy. This may involve scheduling regular breaks, delegating tasks, and engaging in light physical activity. Your healthcare team can provide guidance specific to your individual needs.
Will I experience hair loss during brain radiation treatment?
Yes, hair loss is a temporary side effect of brain radiation treatment. The extent of hair loss may vary, and it usually starts within a few weeks after treatment begins. Hair will typically grow back after treatment is completed, although it may be different in texture or color.
How can nausea and vomiting be managed during brain radiation treatment?
Nausea and vomiting can be managed during brain radiation treatment through various strategies. Your healthcare team may prescribe medications to alleviate these symptoms, recommend dietary changes, and suggest relaxation techniques. It is important to communicate any concerns to your care team for appropriate support.
What can be done to manage headaches and migraines during brain radiation treatment?
Headaches and migraines are known side effects of brain radiation treatment. Your healthcare team may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers, relaxation techniques, or other medications. It is important to discuss the intensity and frequency of headaches with your healthcare team for tailored management strategies.
What are the potential risks associated with swelling and edema after brain radiation?
Swelling and edema can occur in the brain following radiation treatment. These side effects can lead to increased pressure in the skull and potential complications. It is important to monitor and report any symptoms such as severe headaches, changes in vision, or difficulty speaking to your healthcare team promptly.
How can difficulty swallowing and eating be managed during brain radiation treatment?
Difficulty swallowing and eating during brain radiation treatment may require modifications to your diet and eating habits. Your healthcare team may recommend a softer or more liquid diet, swallowing exercises, or the use of feeding tubes. It is crucial to work closely with your healthcare team to ensure proper nutrition and hydration.
What are the emotional and psychological effects of brain radiation treatment?
Brain radiation treatment can have emotional and psychological effects on patients. These may include anxiety, depression, and mood changes. It is important to seek support from your healthcare team and consider counseling or support groups to help manage these effects.
What are the long-term effects of brain radiation on lung cancer?
Long-term effects of brain radiation for lung cancer may include cognitive changes, memory difficulties, and an increased risk of developing other conditions. Regular follow-up care and monitoring can help detect and manage any potential long-term effects.
How can the side effects of brain radiation be managed?
The management of side effects of brain radiation for lung cancer may involve a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and supportive care. It is important to communicate openly with your healthcare team about any side effects experienced to develop an individualized management plan.
Why is effective communication with your healthcare team important during brain radiation treatment?
Effective communication with your healthcare team is crucial during brain radiation treatment to ensure that any side effects or concerns are addressed promptly. Open dialogue allows for the development of strategies to manage side effects and improve quality of life during treatment.