Side Effects of Lung Cancer: Causes and Risk Factors
Lung cancer is one of the most common and serious types of cancer worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. Beyond the challenges of diagnosis and treatment, patients and their families often struggle to understand the wide range of physical and emotional changes that come with the disease. One of the most important aspects to recognize early is the side effects of lung cancer, as these can significantly impact quality of life and treatment decisions.
Understanding the side effects of lung cancer helps you recognize warning signs, seek timely medical care, and manage symptoms more effectively. These side effects may result from the cancer itself, its spread to other organs, or the treatments used to control it. This article provides a comprehensive, easy-to-understand guide to the side effects of lung cancer, from early symptoms to advanced-stage complications.
Overview
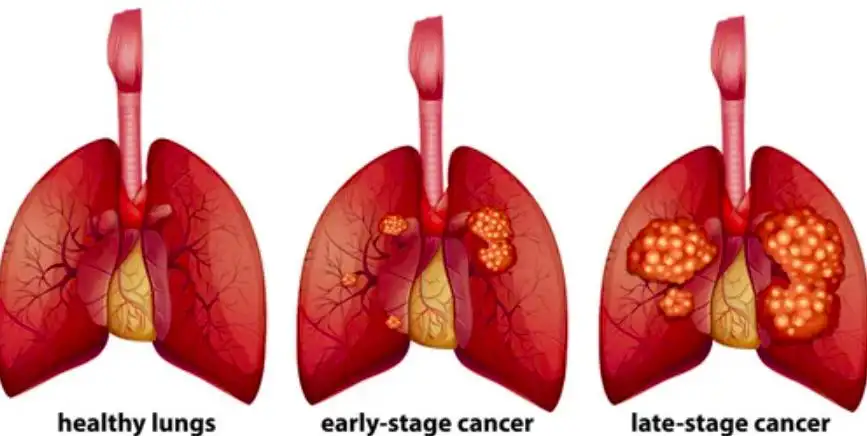
The side effects of lung cancer vary widely depending on the cancer type, stage, location, and the individual’s overall health. Some side effects appear early and are subtle, while others develop as the disease progresses or as a reaction to treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or immunotherapy.
Broadly, side effects can be grouped into:
-
Symptoms caused by the tumor in the lungs
-
Systemic effects affecting the whole body
-
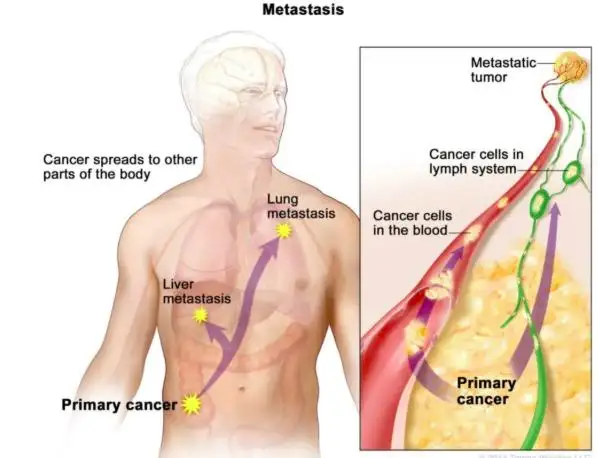
Side effects related to metastasis (cancer spread)
-
Treatment-related side effects
Recognizing these categories helps patients and caregivers better understand what is happening and why certain symptoms occur.
Types
There are two main types of lung cancer, and each can cause slightly different side effects.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
NSCLC is the most common type and tends to grow more slowly. Side effects often develop gradually and may include persistent cough, chest pain, and fatigue.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
SCLC is more aggressive and spreads quickly. Side effects may appear suddenly and be more severe, including rapid weight loss, shortness of breath, and neurological symptoms.
The table below highlights key differences related to side effects:
| Lung Cancer Type | Growth Rate | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Slower | Chronic cough, chest pain, fatigue |
| Small Cell Lung Cancer | Faster | Severe shortness of breath, rapid weight loss, neurological issues |
Causes and Risk Factors
The side effects of lung cancer are closely linked to its causes and risk factors. The most common cause is long-term exposure to harmful substances that damage lung tissue.
Major risk factors include:
-
Smoking and secondhand smoke exposure
-
Exposure to radon gas
-
Air pollution
-
Occupational exposure to asbestos or chemicals
-
Family history of lung cancer
These factors not only increase the risk of developing lung cancer but may also worsen the severity of symptoms and side effects once the disease develops.
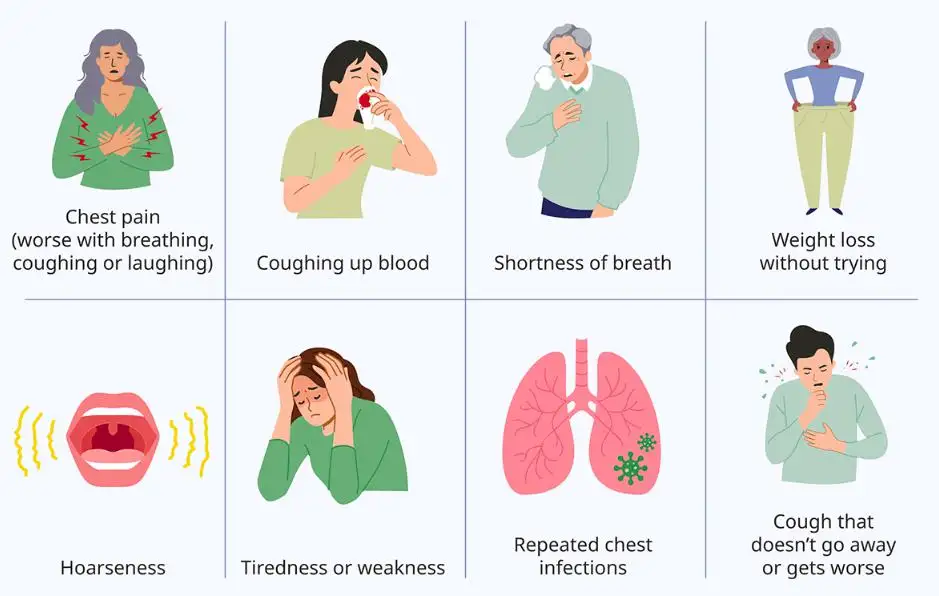
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Early symptoms of lung cancer are often mild and easily overlooked. However, recognizing them early can make a significant difference.
Common early side effects of lung cancer include:
-
Persistent cough that does not go away
-
Shortness of breath during daily activities
-
Chest discomfort or pain
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Recurrent respiratory infections
As the disease progresses, more severe side effects may appear, such as coughing up blood, unexplained weight loss, and hoarseness. Advanced lung cancer can also cause bone pain, headaches, or seizures if the cancer spreads.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing lung cancer and identifying its side effects involves several medical tests and evaluations. Doctors typically begin with imaging tests such as chest X-rays or CT scans to detect abnormalities in the lungs.
Additional diagnostic tools may include:
-
PET scans to detect cancer spread
-
Bronchoscopy to examine airways
-
Biopsy to confirm cancer type
-
Blood tests to assess overall health and organ function
Accurate diagnosis allows healthcare providers to determine whether symptoms are caused by the cancer itself or by treatment-related side effects.
Treatment Options
Treatment for lung cancer aims to control the disease, relieve symptoms, and minimize side effects. The choice of treatment depends on cancer type, stage, and patient health.
Common treatment options include:
-
Surgery to remove tumors
-
Chemotherapy
-
Radiation therapy
-
Targeted therapy
-
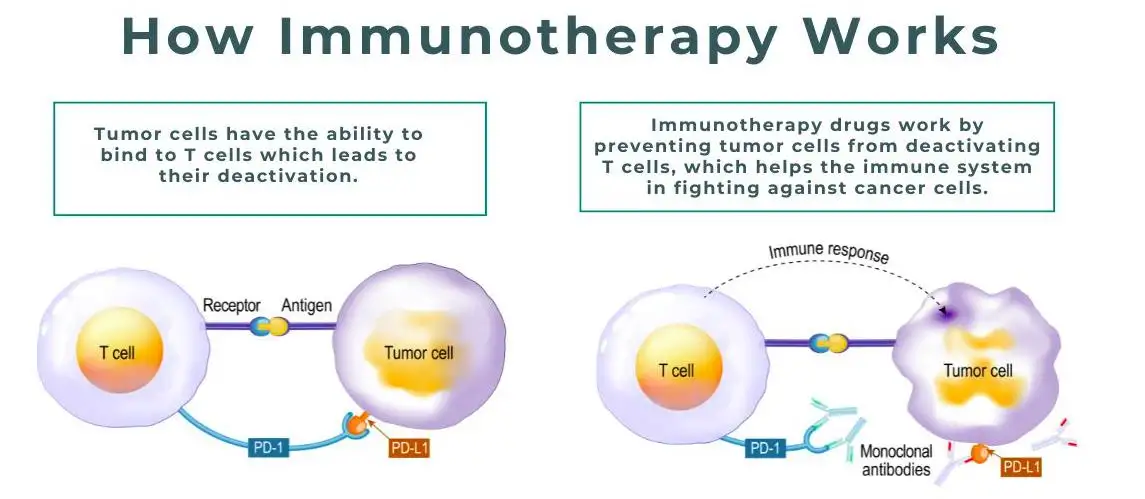
Immunotherapy
Each treatment comes with its own potential side effects. For example, chemotherapy may cause nausea, hair loss, and fatigue, while immunotherapy can lead to immune-related reactions affecting the skin, lungs, or digestive system.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While not all cases of lung cancer can be prevented, certain lifestyle choices can reduce the risk and help manage side effects more effectively.
Recommended strategies include:
-
Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke
-
Maintaining a balanced, nutrient-rich diet
-
Engaging in gentle physical activity as tolerated
-
Reducing exposure to environmental toxins
-
Managing stress through relaxation techniques
Healthy lifestyle changes can improve energy levels, strengthen the immune system, and enhance overall well-being during treatment.
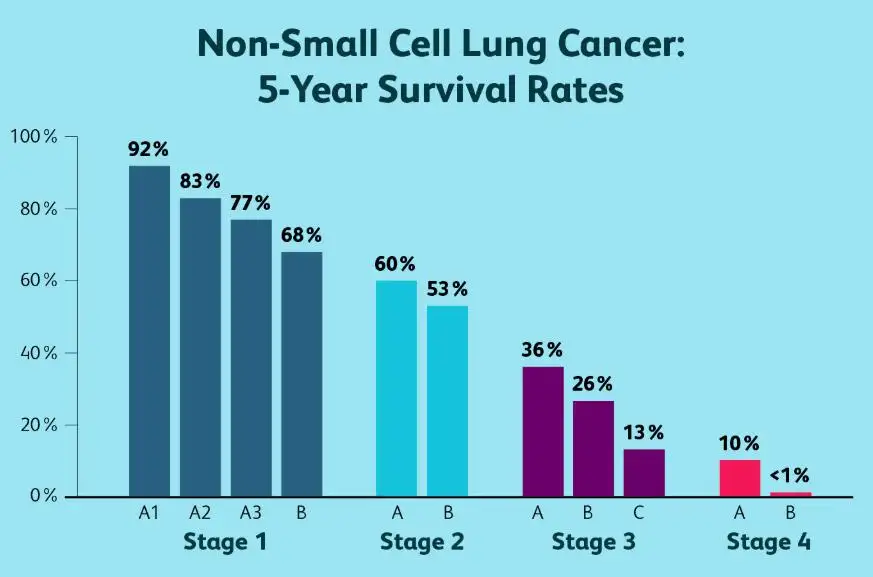
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for lung cancer varies greatly depending on the stage at diagnosis and response to treatment. Early-stage lung cancer has a better outlook, while advanced-stage disease is more challenging to treat.
Survival rates are influenced by:
-
Cancer type (NSCLC or SCLC)
-
Stage at diagnosis
-
Patient age and overall health
-
Access to advanced treatments
Although survival statistics provide general guidance, every patient’s experience is unique, and ongoing medical advances continue to improve outcomes.
Latest Research and Innovations
Recent advances in lung cancer research have led to more effective treatments with fewer side effects. Targeted therapies and immunotherapies are transforming how lung cancer is managed.
Current innovations include:
-
Personalized medicine based on genetic testing
-
New immunotherapy combinations
-
Improved radiation techniques that spare healthy tissue
-
Early detection methods using biomarkers
These developments offer hope for better symptom control and longer survival with improved quality of life.
Coping and Support for Patients
Living with the side effects of lung cancer can be physically and emotionally overwhelming. Emotional support is just as important as medical treatment.
Helpful coping strategies include:
-
Joining cancer support groups
-
Seeking counseling or mental health support
-
Communicating openly with healthcare providers
-
Relying on family and caregiver assistance
Support systems empower patients to manage symptoms, make informed decisions, and maintain a sense of control throughout their journey.
Conclusion
The side effects of lung cancer can affect nearly every aspect of a person’s life, from physical health to emotional well-being. Understanding these side effects enables early detection, better symptom management, and improved communication with healthcare providers.
With ongoing advances in medical research and supportive care, patients today have more options than ever before. Awareness, timely treatment, and strong support systems play a crucial role in improving both survival and quality of life for those affected by lung cancer.
FAQ
What are the most common side effects of lung cancer?
The most common side effects include persistent cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss.
Can lung cancer cause symptoms outside the lungs?
Yes, lung cancer can spread to other organs, causing symptoms such as bone pain, headaches, neurological issues, and liver-related problems.
Are side effects always a sign of advanced lung cancer?
No, some side effects appear in early stages. However, symptoms often become more severe as the disease progresses.
Do lung cancer treatments cause additional side effects?
Yes, treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy can cause side effects, but many are manageable with proper medical care.
How can patients reduce the impact of lung cancer side effects?
Following medical advice, adopting a healthy lifestyle, seeking emotional support, and reporting new symptoms early can significantly reduce the impact of side effects.