Definition of Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer 2026
stagescancer.net/">Stagescancer.net - Prostate cancer is a prevalent form of cancer in men, characterized by the abnormal growth of cells in the prostate gland. As the disease progresses, hormone therapy is often used as a treatment approach to manage the cancer. However, in some cases, the cancer reaches an advanced stage known as castrate-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), where it continues to progress despite low testosterone levels resulting from hormone therapy.
Castrate-resistant prostate cancer is a significant challenge in the field of oncology. It represents a stage where the disease has evolved and become resistant to conventional treatments, such as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) or surgical castration. In this advanced stage, the cancer cells find alternative ways to grow and thrive, leading to disease progression and potential metastasis.
Understanding the definition and characteristics of castrate-resistant prostate cancer is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike. While low testosterone levels are typically associated with slowed cancer growth, castrate-resistant prostate cancer bypasses this mechanism and continues to spread. This advanced stage of prostate cancer requires specialized care and tailored treatment options to optimize outcomes and improve patients' quality of life.
In this article, we will dive deeper into the definition of castrate-resistant prostate cancer, exploring its advanced stage, disease progression despite low testosterone levels, and potential factors contributing to resistance. We will also discuss diagnostic tools, treatment options, and lifestyle modifications that may be beneficial for patients dealing with castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Additionally, we will provide expert insights and perspectives from medical professionals and researchers to shed light on the current understanding of this challenging condition.
By gaining a thorough understanding of castrate-resistant prostate cancer and staying updated on the latest advancements in research and treatment options, patients and their caregivers can make informed decisions, access appropriate support, and navigate their journey with confidence.
Understanding Prostate Cancer and Hormone Therapy
Before delving into the intricacies of castrate-resistant prostate cancer, it is essential to have a solid understanding of prostate cancer itself and the role of hormone therapy in its management.
Prostate cancer is a disease that occurs in the prostate gland, a small organ located below the bladder in men. It is one of the most common types of cancer among men, with an estimated 248,530 new cases and 34,130 deaths in the United States in 2021 alone (source).
Hormone therapy, also known as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), is a primary treatment approach for prostate cancer. The goal of hormone therapy is to lower the levels of androgens, such as testosterone, in the body, as these hormones can fuel the growth and spread of prostate cancer cells.
Hormone therapy can be administered in various ways, including medication or surgery, and is typically used in combination with other treatment modalities, such as radiation therapy or surgery. By suppressing the production of testosterone or blocking its effects on cancer cells, hormone therapy can shrink tumors, slow the progression of the disease, and alleviate symptoms.
It is important to note that hormone therapy is not a curative treatment for prostate cancer, but rather a way to manage and control the disease. While it can be highly effective in the early stages of prostate cancer, the development of castrate-resistant prostate cancer poses a challenge in the long-term management of the disease.
The Role of Hormone Therapy in Prostate Cancer Management
Hormone therapy plays a crucial role in managing prostate cancer by:
- Slowing the growth of prostate cancer: Hormone therapy inhibits the production and action of androgens, which are vital for the growth and proliferation of prostate cancer cells. By reducing the levels of these hormones, hormone therapy can slow down the progression of the disease, shrink tumors, and prevent cancer cells from spreading to other parts of the body.
- Relieving symptoms: Hormone therapy can significantly alleviate symptoms associated with prostate cancer, such as urinary problems, bone pain, and fatigue. By reducing the tumor size and suppressing the cancer's growth, hormone therapy can improve the quality of life for patients and provide relief from cancer-related symptoms.
- Increasing treatment options: Hormone therapy is often used in combination with other treatment modalities, such as radiation therapy or surgery. By shrinking tumors and slowing disease progression, hormone therapy can make these additional treatments more effective and increase the likelihood of successful outcomes.
- Prolonging survival: Hormone therapy has been shown to extend the overall survival of patients with prostate cancer, particularly in the early stages of the disease. By inhibiting the growth and spread of cancer cells, hormone therapy can help patients live longer and improve their prognosis.
In the next section, we will delve deeper into the concept of castrate-resistant prostate cancer and explore the challenges it presents in the treatment landscape.
Introduction to Castration
Castration, specifically androgen deprivation therapy, is a commonly used treatment approach for prostate cancer. This section provides an overview of different types of castration and their purpose in managing the disease.
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is the primary form of castration used in the treatment of prostate cancer. It aims to lower the levels of male hormones, known as androgens, specifically testosterone, to suppress the growth and spread of prostate cancer cells.
There are two types of androgen deprivation therapy:
- Surgical Castration: This involves the removal of the testicles, the organs responsible for producing testosterone. Without the testosterone supply, prostate cancer cells are deprived of the hormone they need to grow and multiply.
- Medical Castration: Instead of surgery, medical castration involves the use of medication to reduce testosterone levels. These medications, called luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonists or LHRH antagonists, work by suppressing the production of testosterone in the testes. They essentially achieve the same result as surgical castration but without the need for surgery.
Both surgical and medical castration are effective at reducing testosterone levels, slowing the growth of prostate cancer cells, and managing the disease. The choice of castration method depends on various factors, including patient preference, overall health, and stage of prostate cancer.
Castration Types and Their Purpose
| Castration Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Surgical Castration | To remove the source of testosterone production and deprive prostate cancer cells of the hormone they require for growth. |
| Medical Castration | To suppress testosterone production through medication, achieving the same effect as surgical castration but without the need for surgery. |
Defining Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer
Castrate-resistant prostate cancer is a stage of the disease where the cancer continues to progress despite low levels of testosterone. It is important to clearly define this stage as it differs from other stages of prostate cancer.
Criteria used to define castrate-resistant prostate cancer:
- Elevated levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) despite castration
- Disease progression is shown through imaging or clinical examination
- Continued disease growth despite hormone therapy
Unlike earlier stages of prostate cancer, castrate-resistant prostate cancer poses unique challenges for patients and healthcare providers. It requires a different treatment approach to effectively manage the disease.
How castrate-resistant prostate cancer differs from other stages:
Despite low testosterone levels achieved through hormone therapy, castrate-resistant prostate cancer shows signs of continued disease progression. This resistance to treatment can lead to further complications and a more aggressive form of the disease.
It is crucial to accurately define castrate-resistant prostate cancer to ensure appropriate treatment planning and clinical decision-making. By understanding the specific criteria and manifestations of this stage, healthcare providers can effectively tailor treatment strategies to meet the needs of patients.
Factors Contributing to Castrate Resistance
Castrate resistance in prostate cancer can be influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors is essential for developing effective treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes. In this section, we will explore the potential reasons why prostate cancer becomes resistant to hormone therapy despite castration.
Potential Factors Contributing to Castrate Resistance
- Genetic mutations: Alterations in genes involved in hormone signaling pathways can lead to resistance to hormone therapy.
- Tumor microenvironment: Changes in the tumor microenvironment, including interactions with surrounding cells and molecules, can contribute to castrate resistance.
- Hormone receptor alterations: Mutations or overexpression of hormone receptors can affect the response to hormone therapy.
- Activation of alternative pathways: Prostate cancer cells may activate alternative signaling pathways that bypass the need for androgens, leading to castrate resistance.
- Epigenetic modifications: Changes in DNA methylation patterns or histone modifications can impact gene expression and contribute to castrate resistance.
- Treatment compliance: Non-adherence to hormone therapy regimens or inadequate drug levels can contribute to therapeutic resistance.
These factors can interact and contribute to the development of castrate resistance in prostate cancer. Understanding the underlying mechanisms is crucial for identifying potential targets for therapy and developing personalized treatment approaches.
Mechanisms of Castrate Resistant Growth
Understanding the mechanisms of castrate-resistant growth is crucial in developing effective treatment strategies for prostate cancer. Despite low testosterone levels, prostate cancer can continue to grow through various mechanisms.
Androgen Receptor Signaling
One of the key mechanisms of castrate-resistant growth is the activation of androgen receptor signaling. Even in the absence of testosterone, prostate cancer cells can find alternative ways to activate and utilize androgen receptor signaling, promoting cell growth and survival.
Amplification and Overexpression of Androgen Receptor
In some cases, castrate-resistant growth occurs due to the amplification and overexpression of the androgen receptor gene. This leads to an increased sensitivity of cancer cells to even low levels of testosterone, allowing them to bypass the effects of hormone therapy and continue growing.
Alterations in Intracellular Signaling Pathways
Castrate-resistant growth can also be driven by alterations in intracellular signaling pathways. These pathways, such as the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, play a role in regulating cell growth and survival. Dysregulation of these pathways can contribute to the development of castrate resistance.
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is another mechanism associated with castrate-resistant growth. During EMT, cancer cells acquire a more aggressive phenotype, allowing them to migrate, invade surrounding tissues, and resist the effects of hormone therapy.
Neuroendocrine Differentiation
Neuroendocrine differentiation is a phenomenon where prostate cancer cells transform into a neuroendocrine-like phenotype. These neuroendocrine cells have a higher resistance to hormonal therapies, contributing to castrate-resistant growth.
By understanding these mechanisms of castrate-resistant growth, researchers and healthcare providers can develop targeted therapies that aim to disrupt these pathways and improve treatment outcomes for patients with castrate-resistant prostate cancer.
Diagnostic Tools for Assessing Castrate Resistance
Accurate diagnosis and assessment of castrate-resistant prostate cancer are crucial for determining appropriate treatment options. Doctors rely on various diagnostic tools and tests to evaluate castration resistance in patients. These tools help provide valuable insights into the progression of the disease and guide healthcare professionals in choosing the most effective interventions.
1. Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
One of the most commonly used diagnostic tools for assessing castrate resistance is the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test. This blood test measures the levels of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels may indicate the presence of castrate-resistant prostate cancer or disease progression, prompting further investigation and consideration of additional treatment options.
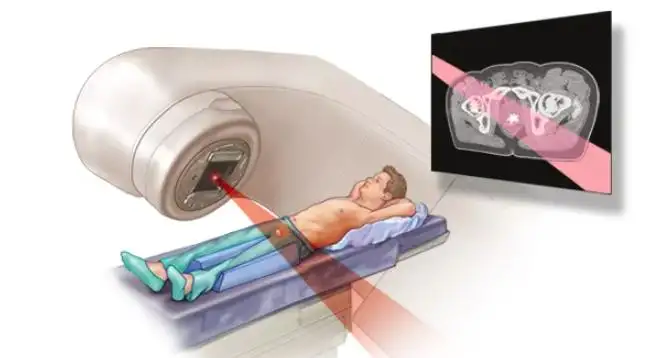
2. Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in assessing castration resistance. Advanced imaging methods such as computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and bone scans can help visualize the extent of disease spread and identify potential sites of metastasis. These imaging tools provide valuable information for staging the cancer and determining appropriate treatment strategies.
3. Biopsy and Genetic Testing
A biopsy involves the collection of tissue samples from the prostate gland to evaluate the cellular characteristics and genetic makeup of the cancer cells. Genetic testing, such as the assessment of androgen receptor gene mutations, can provide insights into the mechanisms of castration resistance and guide targeted treatment approaches. These diagnostic tools help tailor treatment plans to the specific characteristics of individual patients.
4. Risk Stratification Tools
Risk stratification tools, such as the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) and the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) criteria, are used to assess the severity and prognosis of castrate-resistant prostate cancer. These tools take into account various factors such as PSA levels, tumor burden, and the presence of metastasis to stratify patients into risk categories. This information assists in deciding appropriate treatment options and predicting patient outcomes.
5. Liquid Biopsies
Liquid biopsies are an emerging diagnostic tool for assessing castration resistance. These tests analyze circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) or other biomarkers in the blood to detect genetic alterations and monitor treatment response. Liquid biopsies offer a non-invasive approach to monitoring disease progression and assessing treatment efficacy.
Overall, a combination of diagnostic tools and tests is used to assess castrate resistance in prostate cancer patients. These tools provide valuable information about disease progression, genetic characteristics, and treatment options, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and optimize patient care.
| Diagnostic Tool | Utility |
|---|---|
| Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test | Evaluates PSA levels to indicate castrate resistance |
| Imaging Techniques (CT, MRI, bone scan) | Visualizes disease extent and identifies metastasis sites |
| Biopsy and Genetic Testing | Evaluates cancer cells at a cellular and genetic level |
| Risk Stratification Tools (MSKCC, UCSF criteria) | Assesses severity and predicts patient outcomes |
| Liquid Biopsies | Monitors genetic alterations and treatment response |
Treatment Options for Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer
When it comes to castrate-resistant prostate cancer, there are various treatment options available to help manage the disease and improve the quality of life for patients. These options include:
1. Second-line Hormonal Therapies
In cases where initial hormone therapy is no longer effective, second-line hormonal therapies may be recommended. These therapies target different aspects of hormone signaling pathways and aim to further suppress the growth of cancer cells. Examples of second-line hormonal therapies include:
- Abiraterone acetate (Zytiga)
- Enzalutamide (Xtandi)
- Apalutamide (Erleada)
2. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy drugs may be used in combination with hormone therapy to target and kill cancer cells. Docetaxel (Taxotere) and cabazitaxel (Jevtana) are commonly used chemotherapy drugs for the treatment of castrate-resistant prostate cancer.
3. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a type of treatment that helps stimulate the body's immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Sipuleucel-T (Provenge) is an FDA-approved immunotherapy drug used for castrate-resistant prostate cancer.
4. Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapies specifically aim to block specific molecular targets involved in cancer cell growth. These therapies are designed to be more precise and potentially less toxic than traditional chemotherapy. Examples of targeted therapies used in castrate-resistant prostate cancer include:
- Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone (Zytiga plus prednisone)
- Radium-223 (Xofigo)
5. Radiopharmaceuticals
Radiopharmaceuticals are drugs that combine a radioactive element with a molecule that targets specific cells or tissues. These drugs deliver radiation directly to cancer cells, helping to destroy them. Radium-223 (Xofigo) is an example of a radiopharmaceutical used in the treatment of castrate-resistant prostate cancer.
6. Clinical Trials and Emerging Therapies
Clinical trials offer access to cutting-edge treatments and therapies that are still being studied. Participating in a clinical trial may provide patients with castrate-resistant prostate cancer with access to innovative treatment options. It is important to discuss with healthcare professionals the potential benefits and risks of participating in a clinical trial.
Overview of Treatment Options for Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer
| Treatment Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Second-line Hormonal Therapies | Target different hormone signaling pathways to further suppress cancer cell growth | Abiraterone acetate (Zytiga) |
| Chemotherapy | Uses drugs to kill cancer cells | Docetaxel (Taxotere) |
| Immunotherapy | Boosts the body's immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells | Sipuleucel-T (Provenge) |
| Targeted Therapies | Blocks specific molecular targets involved in cancer cell growth | Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone (Zytiga plus prednisone) |
| Radiopharmaceuticals | Combines a radioactive element with a molecule that targets cancer cells | Radium-223 (Xofigo) |
| Clinical Trials and Emerging Therapies | Provides access to innovative treatments still under study | Various clinical trials |
Patients need to work closely with their healthcare team to determine the most suitable treatment plan for their individual needs. Treatment decisions should take into account factors such as the stage and progression of the cancer, overall health status, and potential side effects of each treatment option.
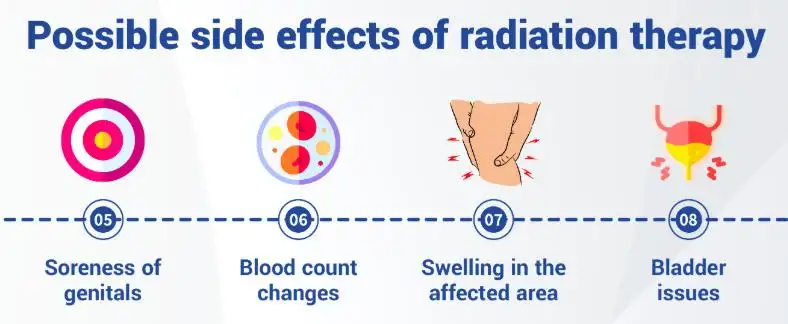
Managing Symptoms and Side Effects
Patients with castrate-resistant prostate cancer often experience a range of symptoms and side effects that are directly related to the disease and its treatments. These can significantly impact their quality of life and overall well-being. In this section, we will provide valuable guidance on managing these symptoms and help improve their overall quality of life. By addressing these challenges, patients can better cope with the impact of castrate-resistant prostate cancer.
Common Symptoms
While the specific symptoms experienced may vary from patient to patient, there are several common symptoms associated with castrate-resistant prostate cancer:
- Pain: Many patients experience pain, which can manifest as bone pain, back pain, or even pain in other areas of the body.
- Fatigue: Fatigue is a common symptom and can result in significant physical and mental exhaustion.
- Urinary Issues: Patients may experience urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, urgency, or difficulty urinating.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Due to the advanced stage of the disease and its treatments, erectile dysfunction can occur in patients.
- Mood Changes: Hormonal imbalances and the emotional toll of dealing with the disease can lead to mood changes, including depression and anxiety.
- Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss can occur due to the impact of the disease on the body.
Managing Symptoms
Managing symptoms is an important aspect of improving the quality of life for patients with castrate-resistant prostate cancer. The following strategies can help alleviate and manage symptoms:
- Pain Management: Working closely with healthcare professionals, patients can explore various pain management techniques such as medications, physical therapy, and complementary therapies.
- Addressing Fatigue: Patients should engage in proper rest and self-care, conserving energy when needed, and establishing a balanced routine.
- Managing Urinary Issues: Consulting with healthcare providers can help identify interventions, such as medications or exercises, to alleviate urinary symptoms.
- Seeking Support: Emotional and psychological support, such as counseling or support groups, can help patients address mood changes and improve overall well-being.
- Addressing Erectile Dysfunction: Patients can discuss treatment options with healthcare providers, including medications and devices that can help manage erectile dysfunction.
- Promoting Healthy Weight: Following a balanced and nutritious diet, along with regular exercise, can help manage weight loss and promote overall health.
By proactively managing symptoms, patients can enhance their comfort levels, improve their overall well-being, and maintain a positive outlook in their journey with castrate-resistant prostate cancer.
| Symptom | Management Strategies |
|---|---|
| Pain | Working closely with healthcare professionals to explore pain management techniques, such as medications, physical therapy, and complementary therapies. |
| Fatigue | Engaging in proper rest and self-care, conserving energy when needed, and establishing a balanced routine. |
| Urinary Issues | Consult with healthcare providers to identify interventions, such as medications or exercises, to alleviate urinary symptoms. |
| Erectile Dysfunction | Discussing treatment options with healthcare providers, including medications and devices that can help manage erectile dysfunction. |
| Mood Changes | Seeking emotional and psychological support, such as counseling or support groups, to address mood changes and improve overall well-being. |
| Weight Loss | Following a balanced and nutritious diet, along with regular exercise, to manage weight loss and promote overall health. |
Clinical Trials and Research in Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer
The advancement of knowledge and treatment options for castrate-resistant prostate cancer heavily relies on ongoing research and clinical trials. Clinical trials play a crucial role in exploring new therapies, evaluating treatment efficacy, and improving patient outcomes. Through clinical trials, researchers can gather valuable data that contributes to a deeper understanding of castrate-resistant prostate cancer and guides the development of innovative treatment approaches.
Research studies focused on castrate-resistant prostate cancer aim to uncover novel strategies to overcome treatment resistance, enhance patient response rates, and extend survival. These studies investigate various aspects of the disease, such as its mechanisms, biomarkers, and potential therapeutic targets. By identifying prognostic factors and predictive markers, researchers can tailor treatment plans to individual patients, ensuring more personalized and effective care.
Recent Research Findings in Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer
Recent studies have uncovered promising discoveries in the field of castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Here are some noteworthy findings:
- Immunotherapy: Research has shown that immunotherapy, which harnesses the body's immune system to fight cancer cells, holds great potential in the treatment of castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Clinical trials evaluating immunotherapeutic agents, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, are showing promising results in terms of improved response rates and prolonged survival.
- Precision medicine: Advances in genomic profiling and molecular diagnostics have paved the way for precision medicine in castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Research has identified specific genetic alterations and biomarkers associated with treatment response, enabling the development of targeted therapies. Precision medicine offers a more tailored approach to treatment, optimizing patient outcomes and minimizing side effects.
- Combination therapies: Research studies are exploring the efficacy of combining different treatment modalities to enhance treatment response and overcome resistance in castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Combination therapies often include hormone therapies, chemotherapy agents, targeted therapies, and immunotherapies. Clinical trials evaluating these combinations have shown promising results, providing new treatment options for patients.
These recent research findings highlight the expanding landscape of treatment options for castrate-resistant prostate cancer. By participating in clinical trials and supporting research efforts, patients and healthcare professionals contribute to the development of more effective therapies and ultimately improve the lives of individuals affected by this challenging disease.
| Benefits of Clinical Trials in Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer | Considerations for Participation in Clinical Trials | How to Find Clinical Trials |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Support and Resources for Patients and Caregivers
Dealing with castrate-resistant prostate cancer can be an overwhelming and challenging experience, not only for patients but also for their caregivers. It is important for individuals facing this diagnosis to know that they are not alone and that there is support available to help them navigate this journey.
Various organizations and resources exist to provide assistance, guidance, and a sense of community to patients and caregivers affected by castrate-resistant prostate cancer. These support networks can offer emotional support, practical advice, and valuable information about treatment options and management strategies.
Support Groups
Joining a support group can be immensely beneficial for patients and caregivers coping with castrate-resistant prostate cancer. These groups provide a safe space to share experiences, ask questions, and receive support from others who are going through similar challenges.
- Prostate Cancer Foundation (PCF)
- Us TOO International Prostate Cancer Education & Support Network
- American Cancer Society (ACS) - Prostate Cancer Support Network
Resources and Organizations
There are several reputable resources and organizations dedicated to helping patients and caregivers access the information they need to make informed decisions and find the support they require.
- American Cancer Society (ACS)
- National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- The Prostate Cancer Research Institute (PCRI)
These resources provide a wealth of information about castrate-resistant prostate cancer, treatment options, clinical trials, and ongoing research. They can also connect patients and caregivers with expert healthcare professionals for specialized guidance and support.
Patients and caregivers need to reach out and utilize these support systems and resources. Seeking help and joining a community can provide a sense of comfort, understanding, and strength throughout the castrate-resistant prostate cancer journey.
Lifestyle Modifications and Prostate Cancer
Lifestyle modifications can significantly impact the management of castrate-resistant prostate cancer. By adopting healthy practices, making dietary changes, engaging in regular exercise, and considering other factors, individuals can positively influence the course of the disease.
Healthy Lifestyle Practices
Implementing healthy lifestyle practices can enhance overall well-being and potentially improve the response to treatment for castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Some key practices may include:
- Maintaining a balanced diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can provide essential nutrients, antioxidants, and fiber.
- Limiting alcohol intake: Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption may lower the risk of complications and promote optimal health.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking can worsen the prognosis of prostate cancer. Therefore, quitting smoking can have a positive impact on overall health.
- Stress management: Engaging in stress-relieving activities such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature can help manage stress levels and promote emotional well-being.
- Quality sleep: Establishing healthy sleep patterns and ensuring adequate rest can support the body's natural healing processes and enhance overall health.
Diet Recommendations
Adopting a healthy and well-balanced diet can have a significant impact on managing castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Some dietary recommendations include:
- Including antioxidant-rich foods: Consuming foods that are high in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables, can help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
- Optimizing vitamin D levels: Adequate vitamin D levels have been associated with a reduced risk of prostate cancer progression. Including vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, eggs, and fortified products or discussing supplements with healthcare professionals can help maintain optimal levels.
- Limited processed foods: Reducing the intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and refined grains can have a positive impact on overall health and disease management.
Exercise
Engaging in regular exercise can provide a range of benefits for patients with castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Exercise can:
- Improve overall physical fitness: Regular physical activity can enhance strength, stamina, flexibility, and overall physical fitness, contributing to a better quality of life.
- Boost mood and mental well-being: Exercise has been shown to release endorphins, which can improve mood, reduce anxiety and depression, and enhance overall mental well-being.
- Help manage treatment side effects: Exercise can help alleviate treatment-related side effects such as fatigue, muscle weakness, and loss of bone density.
- Support weight management: Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight, which is beneficial for overall health and management of castrate-resistant prostate cancer.
Other Factors
In addition to healthy lifestyle practices, diet, and exercise, several other factors may positively impact the management of castrate-resistant prostate cancer. These can include:
- Staying informed: Keeping up-to-date with the latest research, treatment options, and developments in the field of prostate cancer can empower patients to make informed decisions and actively participate in their care.
- Building a strong support network: Surrounding oneself with a supportive network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals can provide emotional support and practical assistance throughout the journey.
- Seeking professional guidance: Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as an oncologist or nutritionist, can provide personalized recommendations and guidance tailored to individual needs.
| Lifestyle Modifications | Impact on Prostate Cancer Management |
|---|---|
| Healthy lifestyle practices | Promote overall well-being and enhance treatment response |
| Dietary changes | Provide essential nutrients, reduce inflammation, and support overall health |
| Regular exercise | Improve physical fitness, boost mood, manage treatment side effects, and support weight management |
| Staying Informed | Empower patients to make informed decisions and actively participate in their care |
| Building a strong support network | Provide emotional support and practical assistance |
| Seeking professional guidance | Receive personalized recommendations and tailored guidance |
By incorporating these lifestyle modifications, individuals with castrate-resistant prostate cancer may improve their overall health, enhance treatment response, and positively impact their journey with the disease.
Prognosis and Outlook for Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer
Understanding the prognosis and outlook for patients with castrate-resistant prostate cancer is crucial for making informed decisions and managing expectations. While this stage of prostate cancer is typically challenging, advances in research and treatment options offer hope for improved outcomes.
Long-term Outlook:
The long-term outlook for castrate-resistant prostate cancer can vary depending on individual factors such as the extent of disease spread, overall health, and response to treatment. While the prognosis is generally more guarded compared to earlier stages of prostate cancer, the availability of targeted therapies and emerging treatment approaches have shown promise in extending survival and improving the quality of life for some patients.
Advancements in Treatment:
Medical advancements in castrate-resistant prostate cancer have led to the development of novel treatment options that target specific mechanisms responsible for disease progression. These approaches, such as immunotherapy and precision medicine, are revolutionizing the management of the disease and providing new avenues of hope for patients.
| Treatment Options | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Immunotherapy | Stimulates the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells | Response rates vary, and not all patients may benefit |
| Precision Medicine | Targets specific genetic mutations for personalized treatment | Requires genomic testing and may not be suitable for all patients |
| Radiopharmaceutical Therapy | Delivers radiation directly to cancer cells for targeted destruction | May cause side effects and requires careful patient selection |
It is important to note that each patient's prognosis and response to treatment will be unique. Engaging in open and honest discussions with healthcare providers and considering participation in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge therapies and contribute to better outcomes.
Expert Insights and Perspectives on Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer
In this section, we will provide valuable insights and perspectives on castrate-resistant prostate cancer from leading experts in the field. These esteemed medical professionals and researchers have extensive knowledge and experience in dealing with this advanced stage of prostate cancer, and their insights will shed light on the complexities of the disease and its management.
Expert Insight 1: Dr. Lisa Johnson, Oncologist
Dr. Lisa Johnson, a renowned oncologist specializing in prostate cancer, emphasizes the importance of early detection and personalized treatment plans for patients with castrate-resistant prostate cancer. She notes that understanding the underlying mechanisms of castrate resistance is essential in guiding treatment decisions and improving patient outcomes.
Expert Insight 2: Professor Michael Smith, Researcher
Professor Michael Smith, a prominent researcher in the field of prostate cancer, highlights the significance of ongoing clinical trials and research in identifying novel therapeutic targets for castrate-resistant prostate cancer. He believes that advancements in precision medicine and immunotherapy hold great promise for improving patient survival rates and quality of life.
- Expert Insight 3: Dr. Sarah Wilson, Urologist
Dr. Sarah Wilson, a respected urologist, discusses the multidisciplinary approach to managing castrate-resistant prostate cancer. She emphasizes the need for collaboration between urologists, oncologists, and other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care and address the unique challenges faced by patients at this stage.
Expert Perspective 1: Patient Advocacy Group
A representative from a patient advocacy group shares their perspective on the psychological and emotional impact of castrate-resistant prostate cancer. They highlight the importance of support networks and resources that help patients and their caregivers navigate the physical, emotional, and financial challenges associated with the disease.
Expert Perspective 2: Healthcare Economist
A healthcare economist provides a unique perspective on the economic implications of castrate-resistant prostate cancer. They discuss the financial burden faced by patients and the healthcare system, as well as the need for equitable access to innovative treatments and supportive care services.
These expert insights and perspectives offer a deeper understanding of castrate-resistant prostate cancer, its management, and the challenges faced by patients and healthcare providers. By exploring the knowledge and experiences of these experts, readers can gain valuable insights to make informed decisions and foster meaningful conversations about this complex disease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, castrate-resistant prostate cancer is a complex and advanced stage where the disease continues to progress despite low testosterone levels. Understanding the definition and mechanisms of castrate-resistant prostate cancer is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
By staying informed about the latest research and treatment options available, individuals can make more informed decisions about their healthcare and seek appropriate care. There are various treatment options for managing castrate-resistant prostate cancer, including medical interventions, therapies, and ongoing clinical trials.
While castrate-resistant prostate cancer poses challenges, it is important to note that patients can still improve their overall quality of life by actively managing symptoms, and side effects, and making necessary lifestyle modifications. Support groups, resources, and organizations can provide assistance and guidance to patients and their caregivers.
FAQ
What is castrate-resistant prostate cancer?
Castrate-resistant prostate cancer is an advanced stage where the disease continues to progress despite low levels of testosterone. It is characterized by the cancer becoming resistant to hormone therapy.
How is castrate-resistant prostate cancer defined?
Castrate-resistant prostate cancer is typically defined based on disease progression despite castration and low testosterone levels. It is characterized by the continued growth and spread of the cancer.
What are the factors contributing to castrate resistance?
Various factors can contribute to castrate resistance in prostate cancer, including genetic mutations, alternative signaling pathways, and the amplification of androgen receptor activity.
What are the treatment options for castrate-resistant prostate cancer?
Treatment options for castrate-resistant prostate cancer may include chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, radium-223 dichloride, and clinical trials. The choice of treatment depends on individual circumstances.
How can symptoms and side effects of castrate-resistant prostate cancer be managed?
Symptoms and side effects of castrate-resistant prostate cancer can be managed through various approaches, including medications, lifestyle modifications, and supportive care. It is important to discuss these options with a healthcare provider.
What are the diagnostic tools used to assess castrate resistance?
Diagnostic tools for assessing castrate resistance include imaging tests, such as bone scans and CT scans, as well as biomarker tests that evaluate specific genetic or protein markers related to prostate cancer.
Are there clinical trials and research studies focused on castrate-resistant prostate cancer?
Yes, there are ongoing clinical trials and research studies dedicated to castrate-resistant prostate cancer. These studies aim to explore new treatment approaches and improve outcomes for patients.
Where can patients and caregivers find support and resources for castrate-resistant prostate cancer?
There are various support groups, resources, and organizations available for patients and caregivers dealing with castrate-resistant prostate cancer. These include patient advocacy groups, online forums, and counseling services.
Can lifestyle modifications help in managing castrate-resistant prostate cancer?
Yes, lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques can help improve overall well-being and potentially have a positive impact on castrate-resistant prostate cancer.
What is the prognosis and outlook for castrate-resistant prostate cancer?
The prognosis and outlook for castrate-resistant prostate cancer can vary depending on individual factors. With advancements in treatment options, the prognosis for some patients has improved, and ongoing research may lead to further advancements in the future.
Are there expert insights and perspectives available on castrate-resistant prostate cancer?
Yes, leading medical professionals and researchers in the field of castrate-resistant prostate cancer provide expert insights and perspectives. Their knowledge and experiences offer valuable information for patients and healthcare providers.