Side Effects of Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Symptoms, and Management
Radiation therapy is one of the most commonly used and effective treatments for prostate cancer. It works by targeting and destroying cancer cells, helping to slow or stop disease progression. While radiation therapy has significantly improved survival rates, many patients understandably worry about the side effects of radiation therapy for prostate cancer and how these effects may impact their daily lives.
Understanding what to expect before, during, and after treatment empowers patients and caregivers to make informed decisions and manage side effects proactively. This article provides a comprehensive, patient-focused overview of the side effects of radiation therapy for prostate cancer, including causes, symptoms, treatment options, and lifestyle strategies to maintain quality of life.
Overview
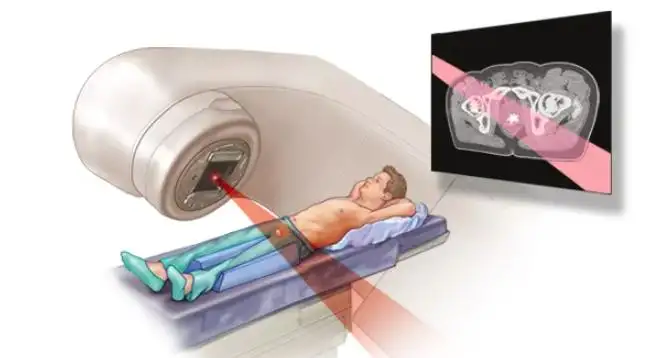
Radiation therapy for prostate cancer uses high-energy rays or particles to damage cancer cells’ DNA, preventing them from growing and dividing. While the treatment is precisely targeted, nearby healthy tissues such as the bladder, rectum, and nerves can also be affected, leading to short-term or long-term side effects.
The severity and type of side effects of radiation therapy for prostate cancer vary from person to person. Factors such as radiation type, dosage, overall health, age, and whether radiation is combined with hormone therapy all influence outcomes.
Types
Radiation therapy for prostate cancer is delivered using different techniques, each associated with specific side effect profiles.
| Type of Radiation Therapy | Description | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) | Radiation delivered from outside the body | Urinary irritation, bowel changes, fatigue |
| Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) | Advanced EBRT with precise dose control | Reduced bowel and bladder side effects |
| Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) | Uses imaging for accurate targeting | Similar to IMRT, often milder effects |
| Brachytherapy (Internal Radiation) | Radioactive seeds placed in the prostate | Urinary retention, erectile dysfunction |
| Proton Therapy | Uses proton beams instead of X-rays | Potentially fewer side effects, still under study |
Causes and Risk Factors
The side effects of radiation therapy for prostate cancer occur when radiation affects healthy tissues near the prostate.
Common causes and risk factors include:
-
High cumulative radiation dose
-
Larger prostate size
-
Pre-existing urinary or bowel conditions
-
Older age
-
Smoking or poor overall health
-
Combination with androgen deprivation therapy (ADT)
Patients with prior prostate surgery or chronic inflammation may also be at higher risk for certain complications.
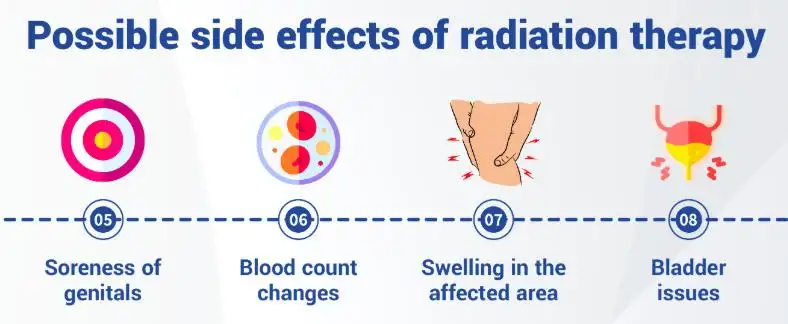
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Side effects may appear during treatment, shortly afterward, or months to years later.
| Affected Area | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Urinary system | Frequent urination, burning sensation, weak stream, blood in urine |
| Bowel and rectum | Diarrhea, rectal bleeding, urgency, discomfort |
| Sexual health | Erectile dysfunction, reduced libido |
| General | Fatigue, skin irritation near treatment area |
Early warning signs such as persistent pain, bleeding, or difficulty urinating should always be reported to a healthcare provider.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of radiation-related side effects is based on:
-
Patient-reported symptoms
-
Physical examination
-
Urine and blood tests
-
Imaging studies (ultrasound or MRI)
-
Endoscopic exams for bowel or bladder issues
Regular follow-up appointments are essential to identify and address complications early.
Treatment Options
Management focuses on symptom relief and preventing long-term damage.
| Side Effect | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| Urinary symptoms | Alpha-blockers, anti-inflammatory medications |
| Bowel issues | Dietary changes, anti-diarrheal drugs, rectal treatments |
| Erectile dysfunction | PDE5 inhibitors, vacuum devices, counseling |
| Fatigue | Exercise programs, sleep optimization |
In severe cases, referral to urologists, gastroenterologists, or sexual health specialists may be required.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While not all side effects are preventable, healthy habits can reduce severity.
Recommended strategies include:
-
Staying well hydrated
-
Following a low-irritant diet during treatment
-
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol
-
Maintaining gentle physical activity
-
Practicing pelvic floor exercises
-
Managing stress through relaxation techniques
Active communication with the care team helps tailor preventive strategies to individual needs.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Radiation therapy offers excellent cancer control for localized and locally advanced prostate cancer. Most side effects are mild to moderate and improve over time. Long-term survival rates remain high, especially when prostate cancer is detected early.
Importantly, advances in technology have significantly reduced the long-term side effects of radiation therapy for prostate cancer, allowing many patients to live full and active lives after treatment.
Latest Research and Innovations
Ongoing research continues to improve safety and effectiveness, including:
-
Adaptive radiation therapy guided by real-time imaging
-
Proton and heavy ion therapy trials
-
Biomarkers predicting radiation sensitivity
-
AI-assisted treatment planning to minimize tissue damage
These innovations aim to further reduce side effects while maintaining strong cancer control.
Coping and Support for Patients
Living with side effects can be emotionally challenging. Support options include:
-
Patient education programs
-
Counseling and mental health support
-
Prostate cancer support groups
-
Sexual health therapy for patients and partners
Seeking support early helps patients feel less isolated and more confident during recovery.
Conclusion
The side effects of radiation therapy for prostate cancer are an important consideration, but they are manageable for most patients with proper care and monitoring. Understanding potential risks, recognizing early symptoms, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly improve quality of life during and after treatment. With modern radiation techniques and ongoing research, outcomes continue to improve, offering both effective cancer control and better long-term well-being.
FAQ
1. Are side effects of radiation therapy for prostate cancer permanent?
Most side effects are temporary and improve within months, although some may persist long term.
2. When do side effects usually start?
Side effects can begin during treatment or shortly after, while some late effects may appear months or years later.
3. Can radiation therapy cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes, erectile dysfunction is a possible side effect, but treatments and rehabilitation options are available.
4. Is radiation therapy safer than surgery?
Both treatments are effective; the choice depends on cancer stage, patient health, and personal preferences.
5. How can I reduce side effects during treatment?
Following medical advice, staying active, eating a balanced diet, and reporting symptoms early can help reduce severity.